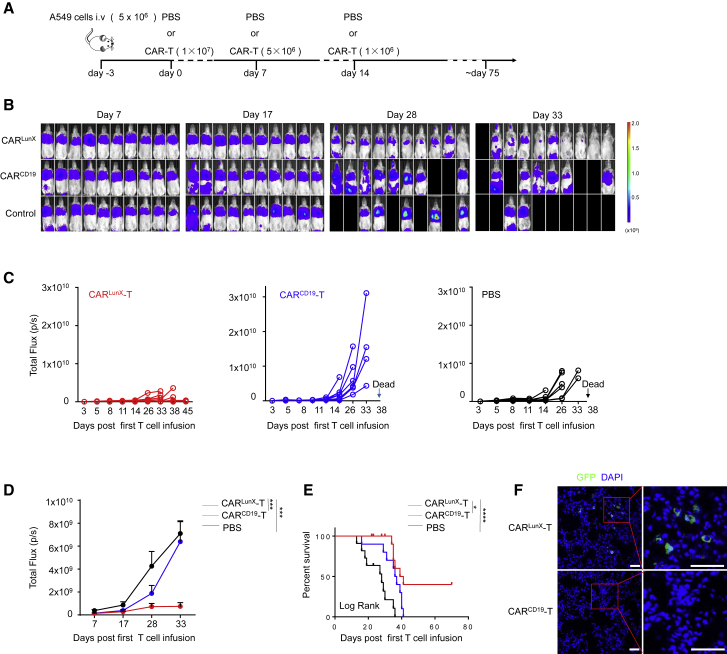
Figure 5.
CARLunX T Cells Inhibit Growth of Lung Cancer Cells and Improve Survival in an Orthotopic Xenograft Model in Mice
(A) Experimental protocol for the A549-xenografted model used in (B)–(F). (B) Representative bioluminescence imaging of B-NDG mice xenografted with luciferase-expressing A549 injected via the tail vein (color map for all images—radiance, minimum = 108, maximum = 2 × 109) and infused (i.v.) with CARLunX T cells or CARCD19 T cells as the experimental protocol from day 7 to day 33. (C and D) Mean flux (D) and individual flux (C) of each group of tumor burden in A549-engrafted CARLunX T cells, CARCD19 T cells, and PBS-treated mice (n = 10 mice, respectively, on day 7) over time. (E) Survival of mice treated with CARLunX T cells (n = 10), CARCD19 T cells (n = 10), or PBS at various times (horizontal axis) after first-time treatment. The survival rate was analyzed by log rank tests. (F) Representative immunofluorescence images using confocal microscopy of tumor-infiltrating CARLunX T cell- and CARCD19 T cell-treated A549 cells. Partially infiltrating CAR-T cells were gated by the red frame. Scale bar, 50 μm.