Figure 4.
Development of a Bone-Homing rAAaV9 Capsid
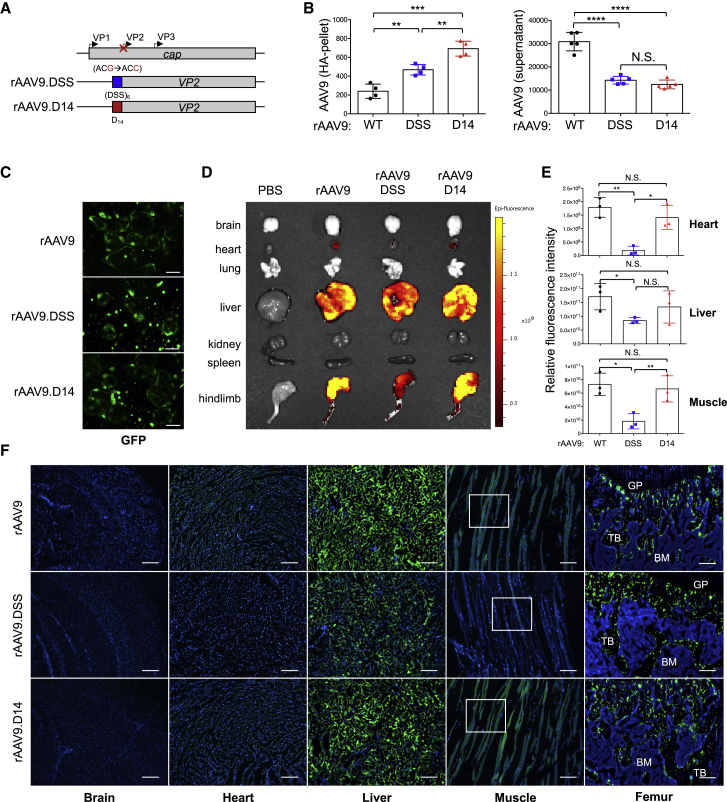
(A) Diagram of constructs for the rationally designed bone-homing rAAV9 capsids. The bone-targeting-peptide motifs ((DSS)6, blue; D14, red) were inserted into the AAV9 capsid at the N terminus of AAV9-VP2 (AAV9.DSS-Nter, AAV9.D14-Nter). cap, capsid proteins. (B) Hydroxyapatite (HA)-binding assay. Vectors (109 GC) were incubated with HA beads for 1 h at 37°C and pelleted by centrifugation at 300 rpm. Vector titers in the pellet and supernatant were measured by ddPCR and normalized to PBS control. (C) Two days after treatment with M-CSF and RANKL, wild-type pre-OCs were transduced with vectors (1011 GC) and then differentiated into mature OCs. Transduction efficiency was assessed by EGFP expression using fluorescence microscopy. Scale bars, 1 mm. (D–F) A single dose of 8 × 1011 GC of vectors was i.v. injected into 2-month-old female mice, and 2 weeks later, EGFP expression in individual tissues was assessed by IVIS 100 optical imaging. (D and E) Representative tissues (D) and relative quantification (E) are displayed (n = 3/group). Scale bars represent relative fluorescence (p/s/cm2/sr/μW/cm2). (F) Alternatively, EGFP expression was assessed by fluorescence microscopy in cryosectioned brain, heart, liver, skeletal muscle, and femur. Boxes indicate areas of high magnification images displayed in Figure S6B. Scale bars, 100 μm. Values represent mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test and one-way ANOVA test. N.S., not significant.