Figure 6.
Bone-Targeting AAV9-Mediated Silencing of ctsk Prevents Bone Loss in a Mouse Model of Senile Osteoporosis
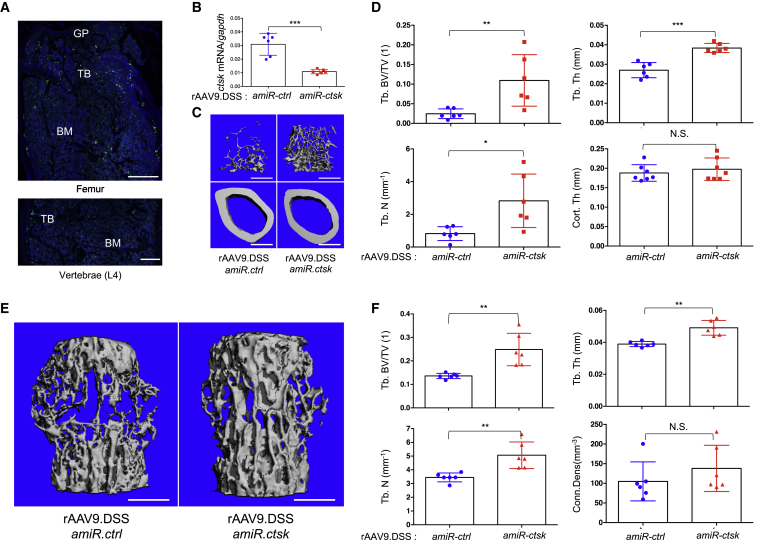
A single dose of 8 × 1011 GC of rAAV9.DSS carrying amiR-ctrl or amiR-ctsk was i.v. injected into 18-month-old male mice. (A) Two months later, EGFP expression in cryosectioned femurs and lumbar vertebrae (L4) were assessed by fluorescence microscopy. (B) Levels of ctsk mRNA in the tibia were assessed by RT-PCR (n = 6/group). Trabecular bone mass and cortical thickness in femurs and lumbar vertebrae (L4) were assessed by microCT. (C–F) Representative 3D-reconstruction (C and E) and relative quantification (D and F) are displayed (n = 6/group). Scale bars, 500 μm. Values represent mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test and one-way ANOVA test. N.S., not significant.