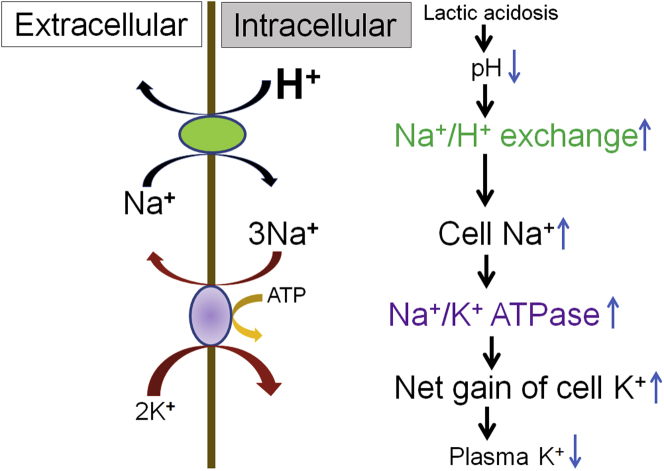
Figure 1.
Schematic of effects of lactic acidosis on plasma K+. Elevation of lactate, an organic acid, causes lactic acidosis, which results in reduction of intracellular pH. The low pH in turn activates the Na+/H+ exchange in the cell, which pushes H+ out in exchange for Na+. The influx of Na+ intracellularly then activates the Na+/K+-ATPase, which results in intracellular shift of K+, leading to hypokalemia. Adapted from Figure 4 in Aronson PS, Giebisch G. Effects of pH on potassium: new explanations for old observations. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:1981–1989.2 Copyright © 2011 by the American Society of Nephrology.