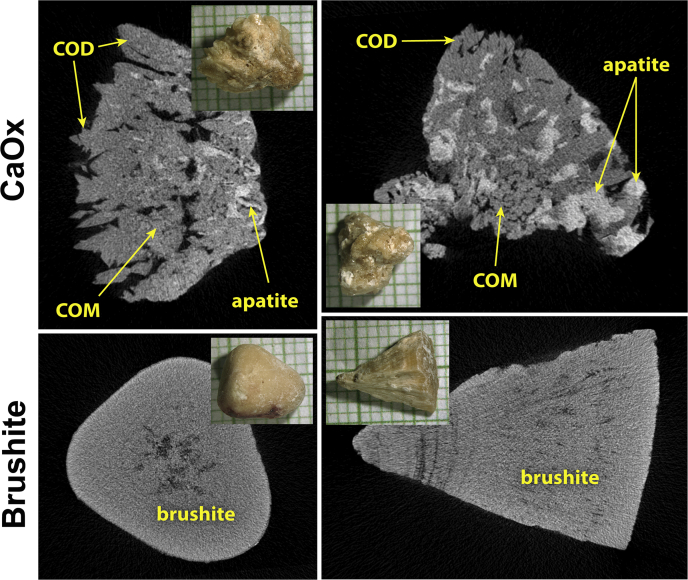
Figure 1.
Micro-computed tomography of kidney stones. Kidney stones are shown in insets, on mm paper. Upper panels show 2 typical calcium oxalate (CaOx) specimens, both of which show polyhedral crystals of calcium oxalate dihydrate (COD) at the surface, calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM; COM and COD can often be distinguished by micro-computed tomography by a combination of crystal shape and apparent x-ray density16) and apatite, which is the most x-ray dense of the minerals commonly found in stones. Specimen in the upper right contained the largest fraction of apatite of any of the specimens used (21% apatite by volume). The lower panels show brushite specimens, both of which were quite pure, which was typical for all the brushite samples.