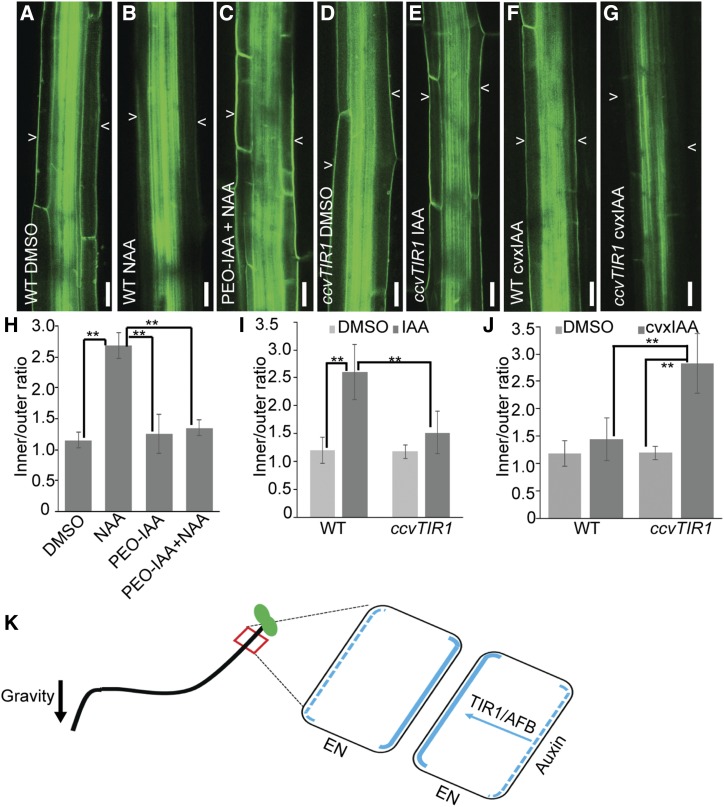
Figure 2.
TIR1/AFB signaling mediates auxin feedback on PIN3 repolarization. A to G, PIN3-GFP localization in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-treated wild-type (WT) hypocotyls (A), 10 μm NAA-treated wild-type hypocotyls (B), 10 μm PEO-IAA and 10 μm NAA co-treated wild-type hypocotyls (C), DMSO-treated ccvTIR1 hypocotyls (D), 10 μm IAA-treated ccvTIR1 hypocotyls (E), 10 μm cvxIAA-treated wild-type hypocotyls (F), and 10 μm cvxIAA-treated ccvTIR1 hypocotyls (G). Arrowheads depict PIN3-GFP at outer side of endodermal cells. Scale bars = 20 µm. H to J, Quantification of PIN3-GFP intensity in wild-type hypocotyls treated with PEO-IAA (H), IAA-treated ccvTIR1 hypocotyls (I), and cvxIAA-treated ccvTIR1 hypocotyls (J). The ratio was calculated by dividing the PIN3-GFP intensity at inner and outer side of hypocotyl endodermal cells. Data and error bars represent the means ± sd. n = 15. **P < 0.05, determined by Student’s test. K, Schematic diagram of auxin receptor TIR1/AFB-mediated PIN3 repolarization for hypocotyl bending termination. At a later stage of shoot gravitropism (24 h), TIR1/AFB mediates auxin perception and facilitates the repolarization of PIN3 to the inner side of endodermal (EN) cells at the lower hypocotyl side, to equalize auxin distribution and thus terminate hypocotyl bending. Blue lines indicate PIN3 distribution at EN cells; the blue arrow indicates auxin-TIR1/AFB-mediated PIN3 repolarization from the outer side (blue dashed line) to the inner side (blue solid line) at the lower-side hypocotyl EN cells; and the black arrow indicates gravity direction.