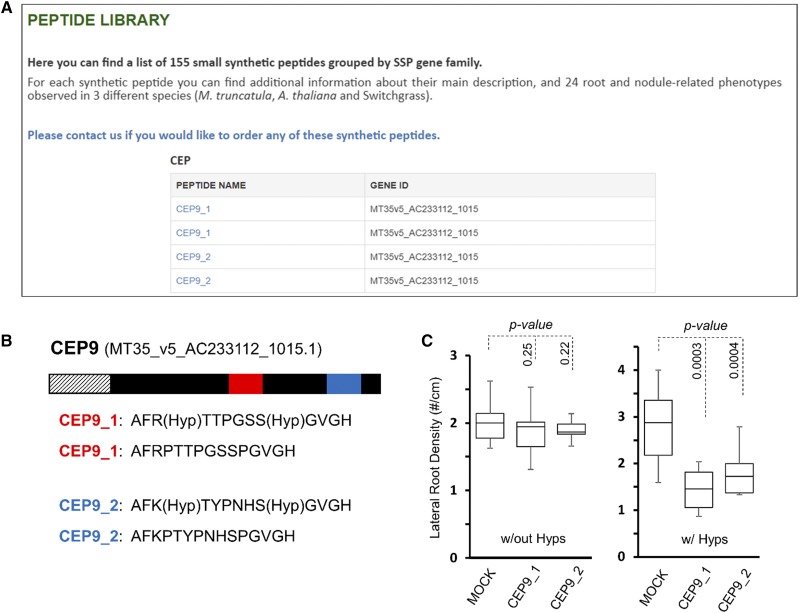
Figure 6.
Surveying the peptide library data reveals the importance of Pro hydroxylation of CEP peptides. A, Hybrid screenshot of the peptide library page of the MtSSPdb showing the four CEP9 peptides investigated here. B, CEP9 encodes a 151-amino acid polypeptide encoding a signal peptide (hashed lines) and containing two CEP domains, designated CEP9_1 (red) and CEP9_2 (blue). The synthetic peptides used for screening are presented below, assuming the presence of Hyp. Peptides lacking Hyp held standard Pro residues at both positions. C, Synthetic peptides from both the upstream and downstream domains strongly inhibit lateral root formation, but only when Pro residues 4 and 11 are hydroxylated. Percentage values indicate the average number of secondary lateral roots in the presence of the indicated peptide relative to the mock-treated control. Plots show the median value (center lines), box limits indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles, and the bars indicate the maximum and minimum values among the data points collected (Students t test). n = 10 for peptide-treated plants and 20 for mock-treated plants.