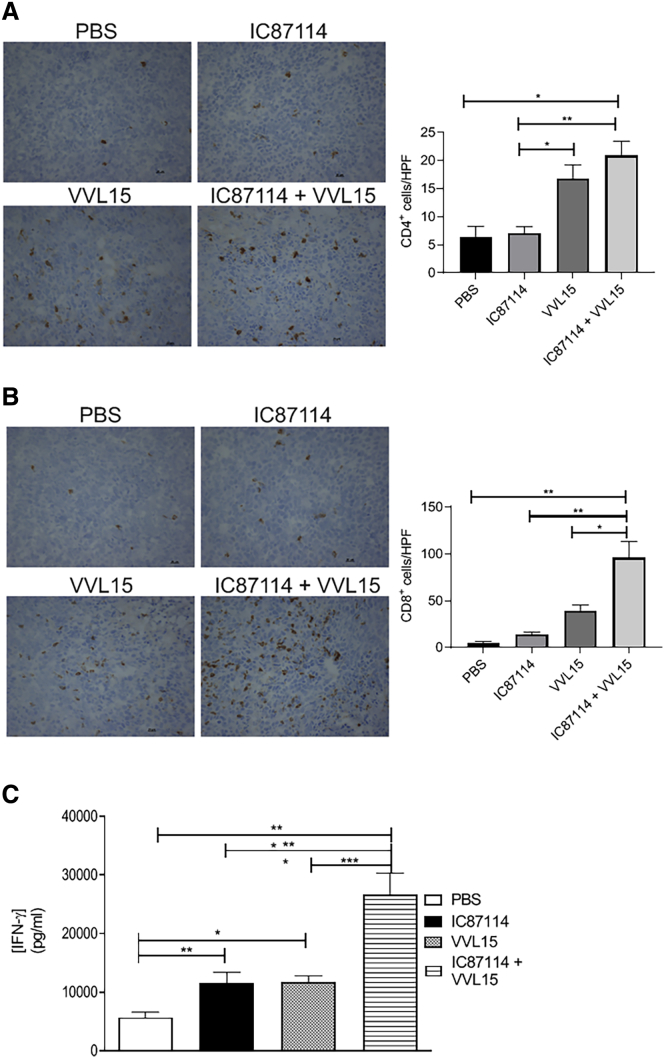
Figure 6.
Pre-treatment with IC87114 Results in Increased T Cell Infiltration and Anti-tumor Immunity In Vivo
CT26 tumors were established in the flanks of immunocompetent BALB/c mice and treated three times 14 days after tumor inoculation (days 1, 3, and 5) with IC87114 (or vehicle buffer) via oral gavage at 75 mg/kg. Three hours later, mice were treated i.v. with PBS or 1 × 108 PFU of VVL15. Animals were sacrificed 3 days post-infection and snap-frozen tumors were stained using antibodies reactive to CD4 (A) or CD8 (B) T cells. Representative images for each condition are shown. 6–12 HPFs were examined for each condition and the CD4+ or CD8+ immune infiltrate was quantified (n = 3/group). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple test correction). (C) Tumors were established and treated as in (A). 7 days post-treatment, spleens were harvested and IFN-γ production by splenocytes was assessed ex vivo (n = 5/group) after stimulation for 7 days with mitomycin-treated CT26 cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test).