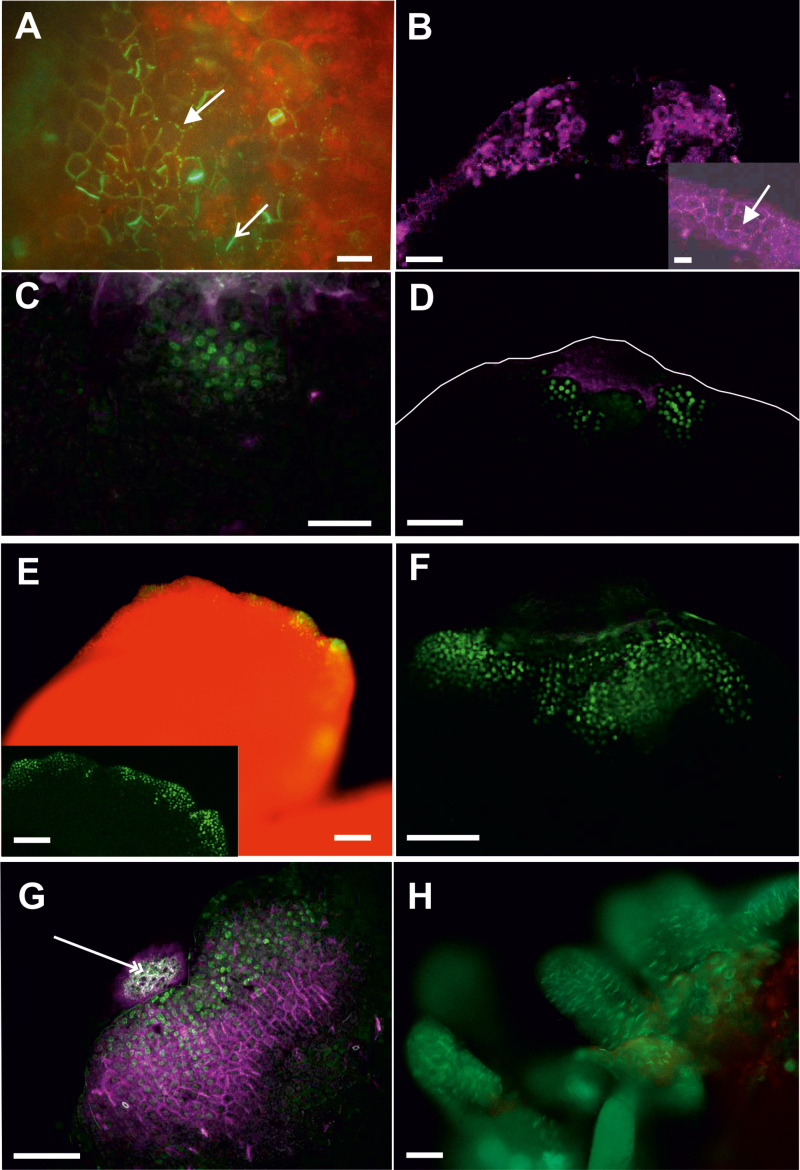
Fig. 7.
Callose deposition precedes WOX2 gene expression during 35S:BBM-induced somatic embryogenesis. (A) Callose staining (green) on the cotyledon tip in 2-day-old 35S:BBM seedlings. Callose is present in PD located in the primary pit fields (arrow) and in the cell plates of newly divided stomatal meristemoids (open arrow). WOX2:NLS-YFP expression was not detected at this stage. (B) Callose staining (purple) along the cotyledon tip and margin in 4-day-old 35S:BBM seedlings. Inset, higher magnification showing callose (arrow). WOX2:NLS-YFP expression was not detected at this stage. (C, D) Five-day-old (C) and 6-day-old (D) 35S:BBM seedlings showing WOX2:NLS-YFP expression (green) and callose staining (purple) in non-overlapping regions. The cotyledon border is marked by a white line. (E, F) Overview of an 8-day-old seedling explant showing WOX2:NLS-YFP expression (green) at the cotyledon margin (E; inset optical section showing gene expression) and tip (F). PD callose (purple) is not detected at this stage in the embryogenic region. (G, H) Callose (purple) and WOX2:NLS-YFP expression (green) colocalize in the same cells as embryogenic protrusions increase in size (G, 10 d old) and differentiate into somatic embryos (H, 12 d old). Scale bars: (A) 30 µm; (D, E inset, F, G) 50 µm; (B, B inset, C) 20 µm; (E, H) 5 mm.