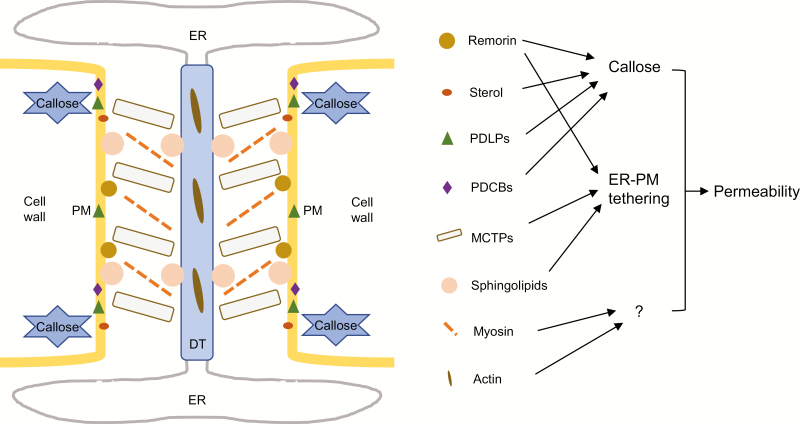
Fig. 1.
A schematic diagram showing the major localized plasmodesmal components that are involved in permeability control. These components are localized at the plasmodesma (left panel, except choline) and modulate plasmodesmal permeability by different mechanisms (right panel). Remorin, sterol, PDLPs, and PDCBs can induce callose biosynthesis and thus restrict plasmodesmal aperture. Remorin, MCTPs and sphingolipids affect the ER–plasma membrane connection and control the cytoplasmic sleeve space. Myosin and actin were previously reported, without a detailed working model, to alter the plasmodesmal permeability. DT, desmotubule; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; MCTP, multiple C2 domains and transmembrane region protein; PDCB, PD CALLOSE-BINDING PROTEIN; PDLP, PD-LOCALIZED PROTEIN; PM, plasma membrane.