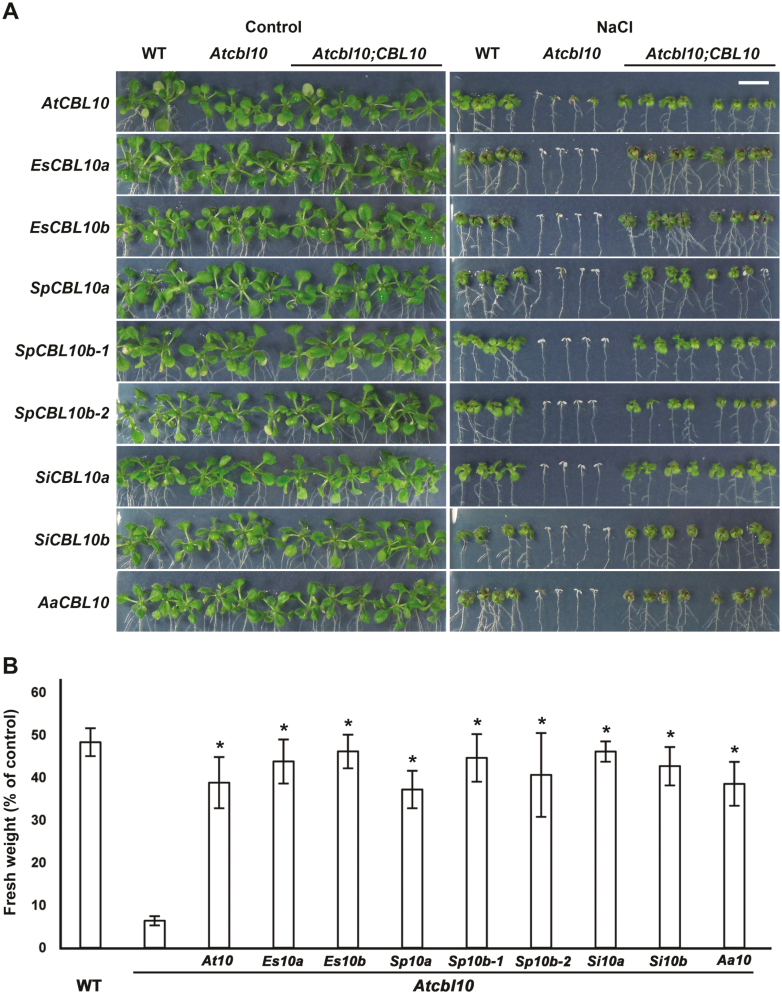
Fig. 4.
CBL10 genes from all Brassicaceae species complement the Atcbl10 salt-sensitive phenotype. CBL10 genes from Arabidopsis (AtCBL10, At10), E. salsugineum (EsCBL10a, Es10a; and EsCBL10b, Es10b), S. parvula (SpCBL10a, Sp10a; SpCBL10b-1, Sp10b-1; and SpCBL10b-2, Sp10b-2), S. irio (SiCBL10a, Si10a; and SiCBL10b, Si10b), and A. arabicum (AaCBL10, Aa10) were expressed in the Atcbl10 mutant, and growth in the absence (control) and presence of salt (125 mM NaCl) was monitored. For salt assays, seeds were germinated on medium without NaCl for 4 d, after which seedlings were transferred to medium without or with the indicated concentration of NaCl. After 10 d of treatment, photographs were taken and total seedling fresh weight was measured. (A) Photographs of the wild type (WT), Atcbl10, and Atcbl10 expressing each CBL10 gene (Atcbl10;CBL10). The scale bar (1 cm, upper right panel) shows the magnification for all images. (B) Total seedling fresh weight was measured to quantify growth and is presented as a percentage of control. Data are means ±SE of at least 24 seedlings per genotype grown in three independent experiments. *Complementation of the Atcbl10 salt-sensitive phenotype (Tukey–Kramer HSD, P≤0.05).