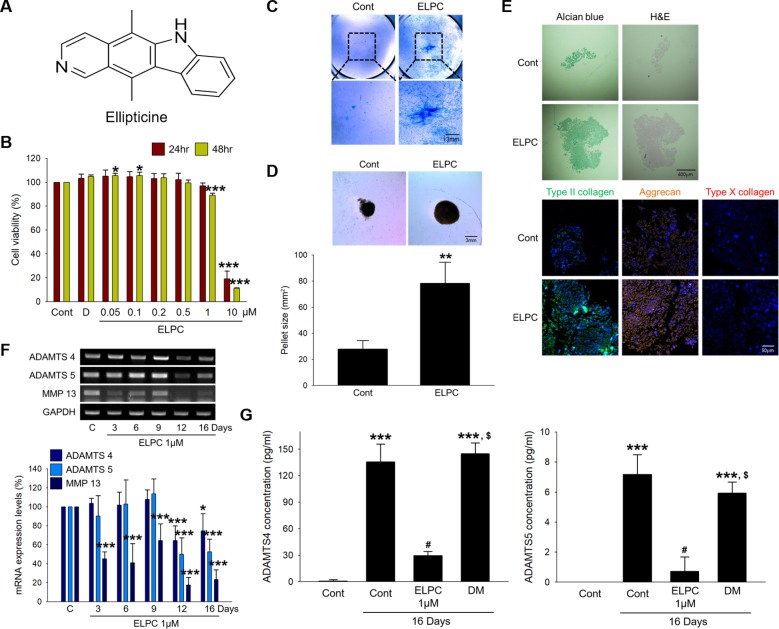
Fig. 3. Ellipticine induces chondrogenic differentiation in ASCs.
a Structure of ellipticine. b Concentration-dependent cell viability was measured by cell viability assays in ASCs. D DMSO-treated ASCs *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 compared to the control. n = 3. c The ability of ELPC to induce differentiation was confirmed using Alcian blue staining after ASCs were incubated with ELPC for 16 days. Scale bar: 3 mm. d A 3D pellet culture was performed using ASCs or ELPC-treated ASCs for 16 days. **p < 0.01 compared to the control. n = 3. e The untreated ASC and ELPC-treated ASC pellets were stained using Alcian blue and H&E. The expression of Type II collagen, Aggrecan, and Type X collagen was detected by immunofluorescence. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (Blue). Scale bar: upper 400 μm and lower 50 μm. f The mRNA expression of the extracellular matrix degradation enzymes ADAMTS4, ADAMTS5, and MMP13. Normalized by GAPDH. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 compared to the control. n = 3. g The concentrations of secreted ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 were measured by ELISAs. ***p < 0.001 compared to the control, #p < 0.001 compared to the 16-day control, $p < 0.001 compared to the ELPC-treated ASCs. C and Cont control, DM chondrogenic differentiation induction medium, ELPC ELPC-treated ASCs. n = 3.