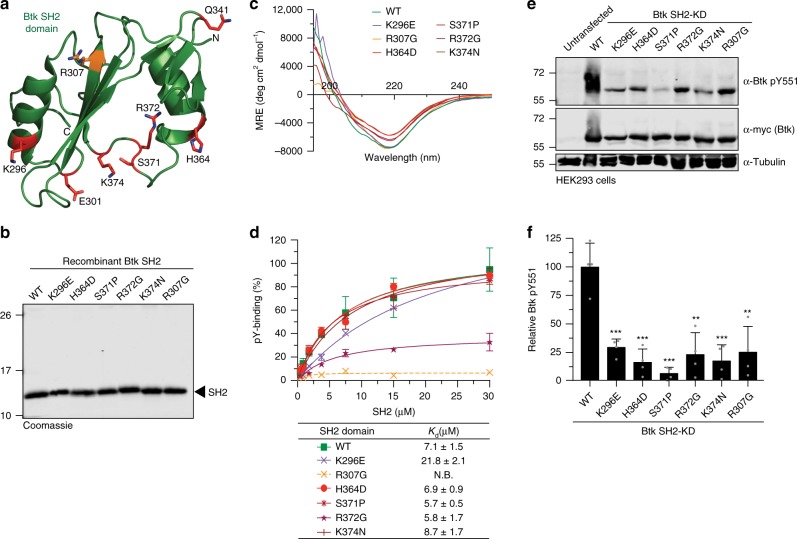
Fig. 1. Mutations in Btk SH2 domain abrogates pY551 phosphorylation.
a Mapping of a subset of XLA-patient mutations (red sticks) onto the human Btk SH2 domain structure (PDB 2GE9). The residue R307 (orange sticks) is part of the pY-binding motif (FIVRD). Here and in all subsequent figures, the residue numbering refers to full-length human Btk. b Representative SDS-PAGE analysis of recombinant wild-type and mutant Btk SH2 domains purified from E. coli. c Averaged far-UV circular dichroism (CD) spectra of recombinant wild-type and XLA mutant Btk SH2 domains. Mean residue ellipticity (MRE) for each protein was calculated from three independent measurements. d Binding of a fluorescently labeled pY-peptide to recombinant Btk SH2 domains. Indicated Kd values were obtained from the fitting to a 1:1 binding model. Data are mean ± SD of two technical replicates. Non-binding (N.B). e HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with a construct containing an N-terminal 6xMyc-tagged human Btk SH2-KD wild-type or mutants. Immunoblotting of cell lysates was performed to assess Btk pY551 phosphorylation. f Quantification of pY551 immunoblot shown in e and normalized to total Btk (Myc) expression. Data are mean ± SD of three biological replicates (n = 4) and P-values were calculated using an unpaired t-test. **P ≤ 0.01 and ***P ≤ 0.001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.