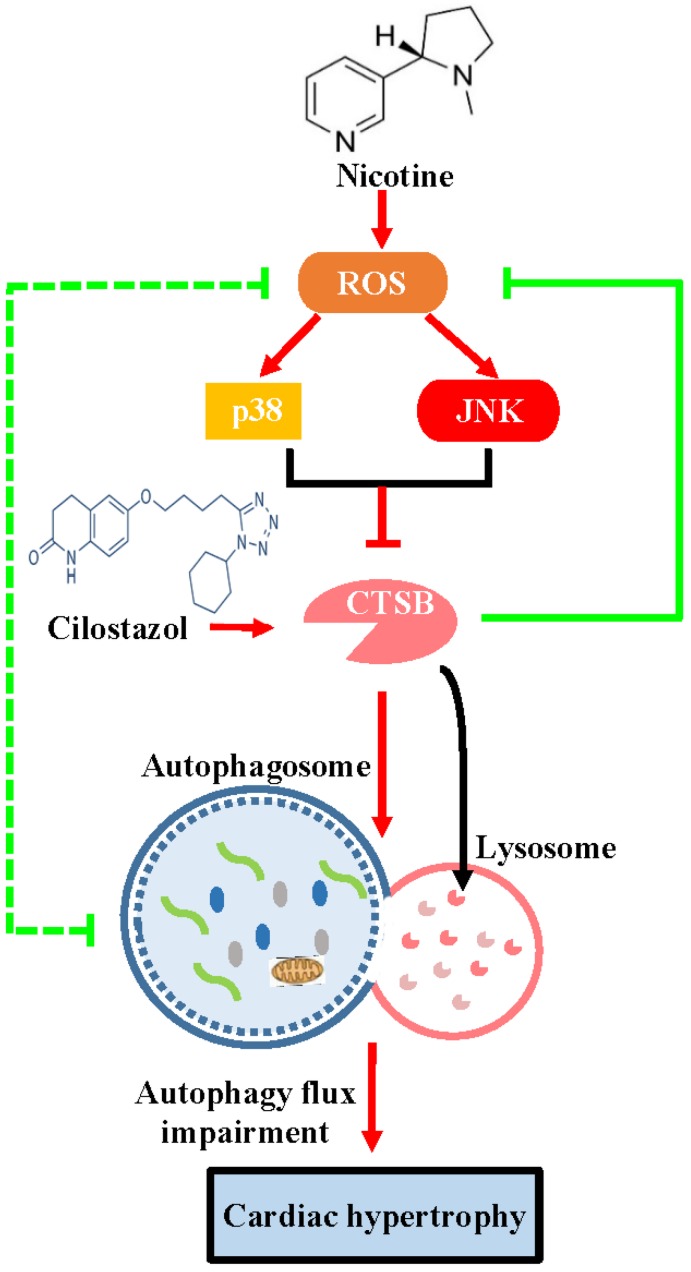
Figure 8.
The schematic diagram of cilostazol's modulation on nicotine-induced autophagy impairment and cardiomyocytes hypertrophy through CTSB/ROS/p38MAPK/JNK pathway. Nicotine activates ROS/p38/JNK signaling and decreases the CTSB activity, which inhibits the fusion of autophagosome and lysosome. Just as the dashed green line showed, a negative feedback exists between ROS and autophagy flux impairment: ROS impairs the fusion of autophagosome and lysosome, and the impaired autophagy flux lead to the ROS accumulation. The nicotine-induced impaired autophagy flux leads to cardiomyocytes hypertrophy in NRVMs. Cilostazol rescues the nicotine-induced ROS accumulation, then dephosphorylates p38/JNK, alleviates autophagy impairment through stimulating CTSB activity and improves cardiomyocytes hypertrophy ultimately.