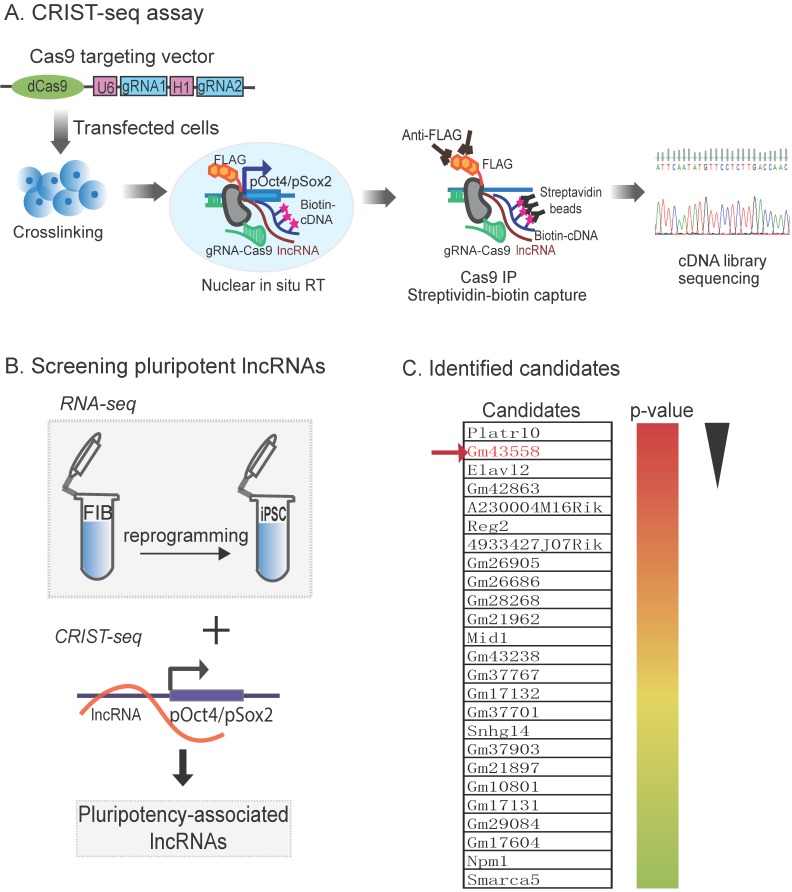
Figure 1.
Mapping pluripotency-associated lncRNAs by RNA-seq and CRIST-seq. A) Chromatin-lncRNA in situ reverse transcription trap sequencing (CRIST-Seq) assay. dCas9: Catalytically inactive CRISPR Cas9; FLAG: a tag octapeptide at the N-terminal of Cas9; gRNA: Cas9 gRNAs that target the Oct4/Sox2 promoter. After fixation, the Oct4/Sox2 promoter-interacting RNAs were reverse transcribed into cDNAs in the isolated nuclei with biotin-dCTP. The Cas9 Oct4/Sox2 promoter biotin-cDNA complex was immunoprecipitated by a Cas9-FLAG antibody, and biotin-cDNAs were further purified from genomic DNAs by biotin-streptavidin beads. The CRIST-captured cDNAs were used for Illumina library sequencing to identify the RNA components in the Oct4 and Sox2 promoters. B) Profiling pluripotency-associated lncRNAs by CRIST-seq and RNA-Seq. The Oct4/Sox2-interacting lncRNAs identified by CRIST-seq were integrated with RNA-seq data. The combination of these two datasets helps identify lncRNAs that interact with the Oct4 and Sox2 promoters and are also expressed differentially in reprogramming. C) Pluripotency-associated RNA candidates identified by RNA-Seq and CRIST-Seq. The RNA candidates are ranked on the basis of the RNA expression-fold between fibroblasts (FIBs) and iPSCs from the high (red) to the low (blue). Gm43558 (Osblr8) was chosen for further studies.