Figure 5:
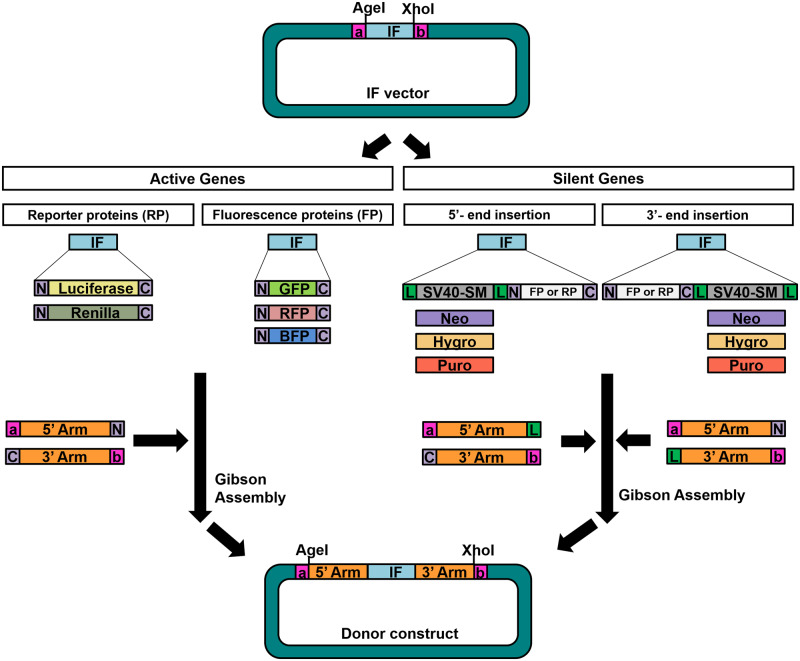
The donor vector bank provides various tools for studying different types of genes using the CRISPR knock-in technique. The IF donor vector is basically composed of a linker pair and an IF. For active genes, the IF is usually an RP or an FP. The protein linkers are optional components added based on investigators’ purposes. As for silent genes, an additional removable SM (LoxP-SM-LoxP) is required for colony selection. Thus, the IF vector has an RP/FP placed before or after a removable SM. In the donor vector bank, the options for the IF vectors are Luciferase, Renilla, GFP, RFP, or BFP. For SM, the vectors with Neomycin-, Hygromycin-, or Puromycin-resistance gene are ready. Consequently, researchers pick an IF vector and then insert the 5’/3’ homologous arm of the knock-in target genes. With the presence of the linker pair and the vector bank, donor constructs can be produced quickly and cost-effectiveness. N: protein linker N, C: protein linker C, Neo: Neomycin-resistance gene, Hygro: Hygromycin-resistance gene, Puro: Puromycin-resistance gene, L: LoxP, SV40-SM: SV40 promoter and the SM, a: linker pair a, and b: linker pair b.