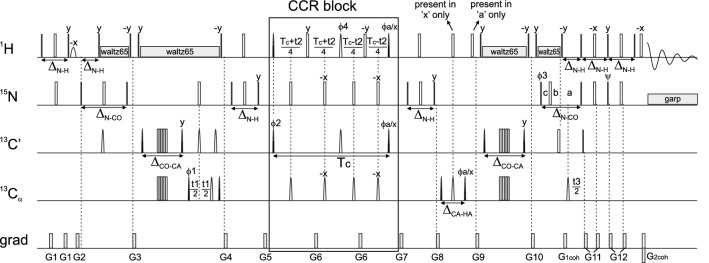
Fig. 1.
Pulse sequence of the experiment for the dd – C CSA CCR rate measurement. evolution is in real-time mode, C evolution is in constant-time mode and N evolution is in semi-constant time mode: , , . The delays were set as follows: , , , , . Unless noted explicitly, pulse phases are set to x. Phase depends on the version of experiment; for reference experiment x, for cross experiment y. 16-step phase cycle was used: = x, -x, = 2(x), 2(-x), = 4(x), 4(y), 4(-x), 4(-y). Receiver phase . Selective pulses affecting only nuclei were pc9 (Kupce and Freeman 1994) for pulses and reburp (Geen and Freeman 1991) for pulses. Simultaneous inversion of and C spins was achieved using 6-element composite pulse (Shaka 1985). Selective pulses for C and nuclei were q5 (for pulses) and q3 (for pulses) (Emsley 1969). The pulses labelled ”present in ’a’/’x’ only” were executed only in reference/cross version of the experiment, respectively