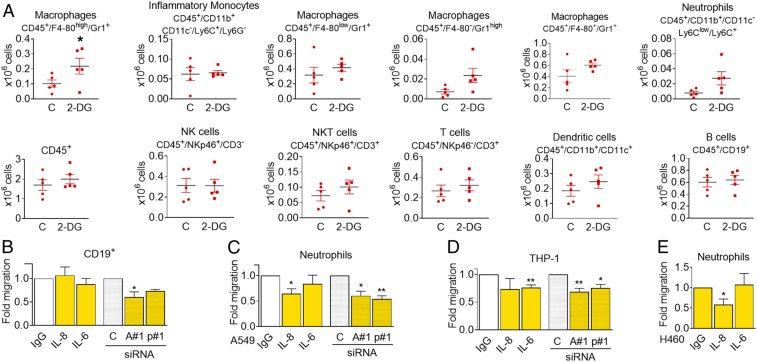
Fig. 7.
Conditioned medium from starved cells alters immune cell composition in the peritoneal cavity. (A) Conditioned medium from CT26 cells that had been incubated for 48 h with or without 25 mM 2-DG was cleared by centrifugation and further concentrated 20 times. Then 350 µL of this medium were injected intraperitoneally every 24 h. Forty-eight hours after the first injection, peritoneal cells were isolated and subjected to FACS analysis using the indicated markers. Asterisks denote significance using Student t test (P < 0.05). (B) PBMCs were plated in the top of Boyden chambers and allowed to migrate to conditioned media from glucose-deprived A549 cells (0 mM glucose, 24 h) previously transfected for 40 h with nontargeting siRNA (control, “C”), ATF4#1 (“A#1”), or p65#1 (“p#1”), or toward conditioned medium from glucose-deprived A549 cells containing control unspecific immunoglobulin G (IgG) or neutralizing antibodies against ("α") IL-6 or IL-8. CD19+ cells were measured by FACS analysis 20 h later. Results show mean ± SEM of four to six experiments. Asterisks denote significant differences between each treatment and its siRNA or antibody control. (C and D) Neutrophils or differentiated THP-1 were allowed to migrate to media described in B for 2 or 20 h, respectively, and counted. Data show mean ± SEM of five to six experiments. Asterisks denote significant differences between each treatment and its siRNA or antibody control. (E) Conditioned media of H460 cells starved for 24 h (0 mM Glc, 2% FBS) were incubated with unspecific IgG or neutralizing antibodies against IL-6 or IL-8 and placed in the bottom of a Boyden chamber. Neutrophils extracted from human blood were allowed to migrate for 1 h and counted. Results show mean ± SEM (n = 4–6) experiments. Asterisks denote significant differences between IgG and each treatment. Error bars represent the SEM. The significance was indicated as follows: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.