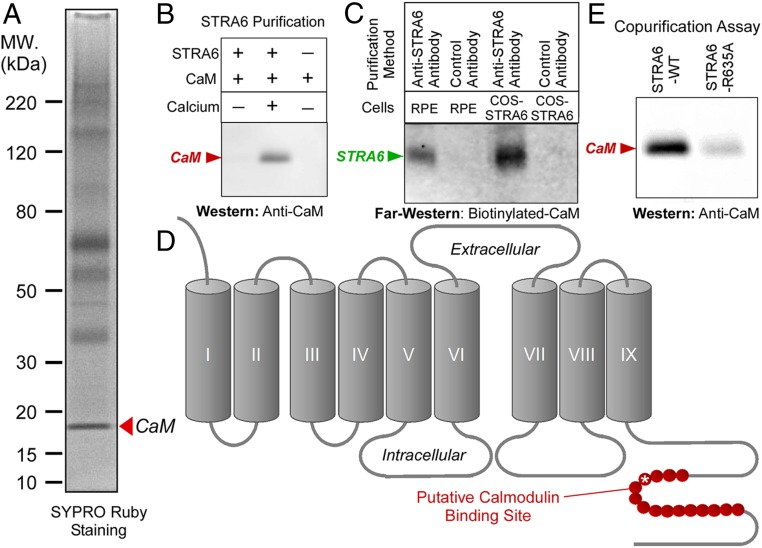
Fig. 1.
Unbiased identification of STRA6-interacting proteins in the native RPE cells using mass spectrometry. (A) STRA6 was purified from RPE cells freshly dissected from bovine eyes by immunoaffinity purification using an antibody against bovine STRA6. Mass spectrometric analysis revealed that most of the stained bands are STRA6 itself. A distinct band with an apparent molecular mass of about 18 kDa was identified as calmodulin (arrowhead). (B) Calcium-dependent interaction between STRA6 and calmodulin. Calmodulin copurifies with STRA6 only when calcium is present. (C) Calmodulin overlay assay. Biotinylated-calmodulin specifically binds to STRA6 on nitrocellulose membrane. STRA6 was purified from RPE cells or COS-1 cells expressing STRA6 using anti-STRA6 antibody. Negative control is an antibody that does not bind STRA6. (D) The computer-predicted calmodulin binding site on STRA6 is shown in red in the STRA6 topology. (E) The R635A mutation in the putative calmodulin binding site (asterisk in D) significantly suppresses calmodulin binding of STRA6, as shown by copurification of calmodulin with STRA6.