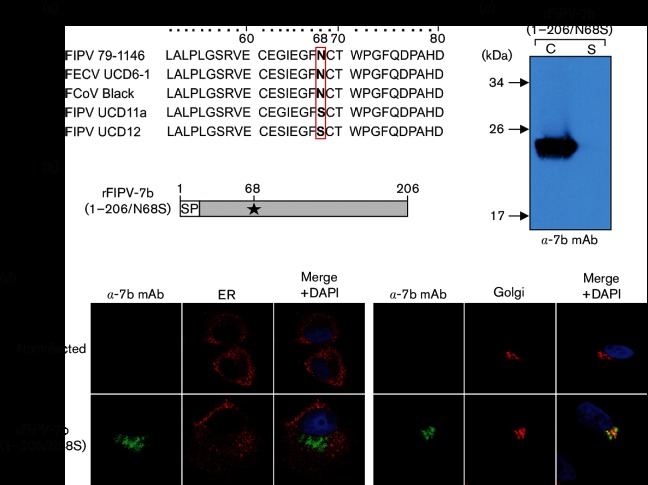
Fig. 1.
Detection of accessory protein 7b in FIPV-infected cells by anti-7b monoclonal antibody 14D8 (α−7b mAb). (a) Sequence alignment of amino acids (aa) 51–80 in 7b. FIPV 79–1146 (AY994055), FECV UCD6-1 (ACR46154), FCoV Black (EU186072), FIPV UCD11a (ACR10287.1) and FIPV UCD12 (ACR10305.1). AA position 68 is highlighted. (b) Schematic representation of the 7b protein encoded by rFIPV-7b(1–206/N68S). The Asn-to-Ser substitution at position 68 (N68S) is indicated by an asterisk. SP, signal peptide; numbers indicate amino acid positions in 7b. The arrow represents the predicted signalase cleavage site between residues 17 and 18. (c) CRFK cells were infected with rFIPV-7b(1–206/N68S)at an m.o.i. of 0.1. Cells and cell culture supernatant were harvested at 16 h p.i. Cell lysate (C) and cell culture supernatant (S) were separated by SDS-PAGE (10 %) under reducing conditions and analysed by Western blotting using anti-7b mAb. (d) CRFK cells were mock-infected or infected with rFIPV-7b(1–206/N68S)at an m.o.i. of 1. Cells were fixed at 16 h p.i. and analysed by confocal laser-scanning microscopy. Immunofluorescence staining of 7b was performed with anti-7b mAb (green signal). Immunofluorescence staining of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (left panel, red signal) and the Golgi complex (right panel, red signal) is shown. Cell nuclei (blue signal) were stained with DAPI.