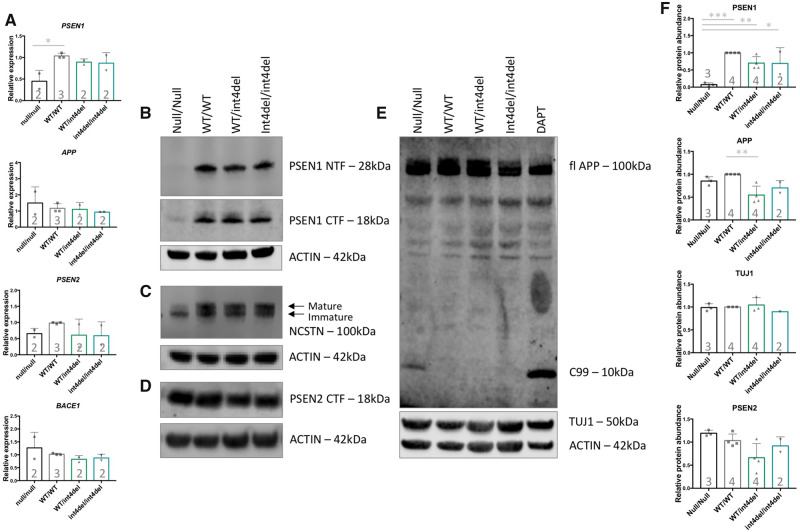
Figure 3.
Analysis of γ-secretase and APP processing in iPSC-derived neurons. (A) PSEN1, PSEN2, APP and BACE1 expression in iPSC-derived neurons 100 days post-induction was assessed by qPCR in neurons from PSEN1 knockout, PSEN1 wild type, PSEN1 int4del heterozygous and PSEN1 int4del homozygous lines. PSEN1 expression was significantly reduced in the PSEN1 knockout neurons. No significant differences in PSEN2, APP and BACE1 were observed. (B–E) Western blot on whole cell lysates of day 100 neurons was used to analyse protein levels of PSEN1 N-terminal fragments (28 kDa), PSEN1 C-terminal fragments (18 kDa), NCSTN (100 kDa), PSEN2 C-terminal fragments (18 kDa), APP (100 kDa) and neuronal marker TUJ1 (50 kDa). The DAPT sample represents an unrelated control line treated with the γ-secretase inhibitor DAPT at 10 μM for 48 h. (F) Quantification of western blot band intensities in B–E. PSEN1 protein abundance is significantly reduced in PSEN1 knockout lysates and APP is significantly increased in the corrected wild-type neurons compared with parental PSEN1 int4del. *P > 0.05, **P > 0.01, ***P > 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Numbers within histograms represent the number of independent neural inductions.