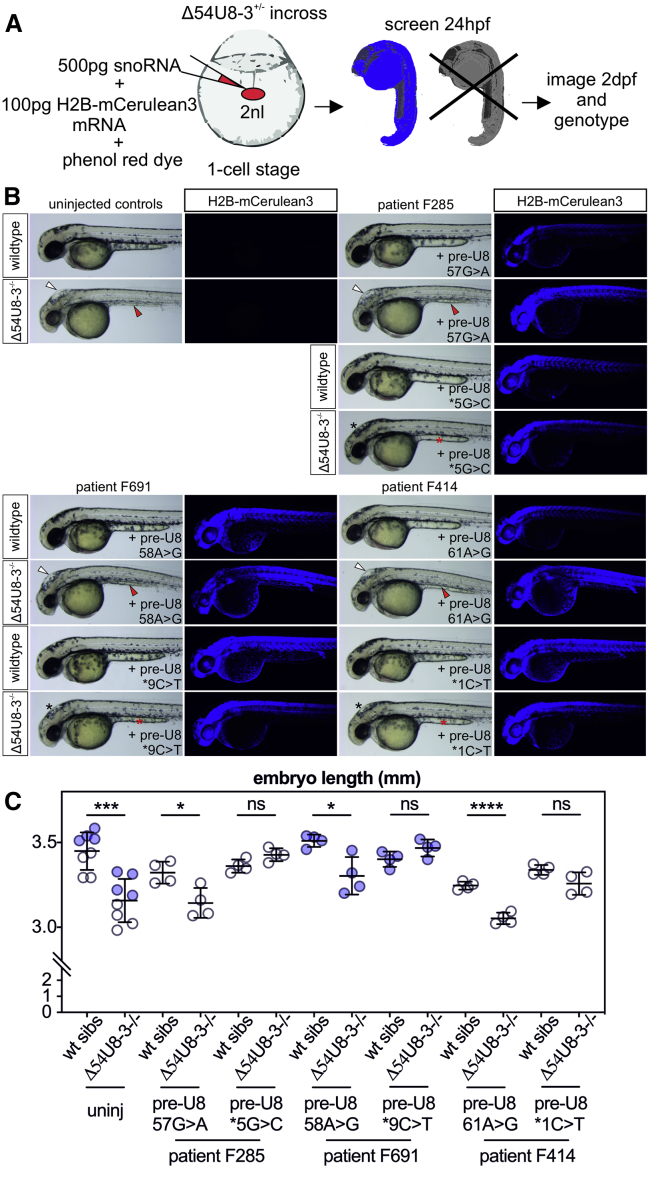
Figure 4.
Functional Testing of LCC Mutant U8 snoRNAs Identifies One Null and One Functional Allele
(A) Schematic depicting the experimental design for transient ubiquitous expression of U8 small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) mutants and H2B-mCerulean3 mRNA. Bolus size is monitored through the use of phenol red dye and successful uptake of the microinjected solution into the animal pole is traced using nuclear cerulean fluorescence.
(B) Leukoencephalopathy with calcifications and cysts (LCC) mutant snoRNAs specific to the region required for 15.5K binding (n57, n58, and n61) fail to rescue the hindbrain swelling (white arrowheads) and yolk extension (red arrowheads) of Δ54U8-3 mutants, whereas LCC mutants specific to the 3′ extension (n∗1, n∗5, and n∗9) rescue hindbrain swelling (black asterisks), yolk abnormalities (red asterisks), and pigmentation defects.
(C) LCC mutant snoRNAs specific to the region required for 15.5K binding (n57, n58, and n61) do not rescue the reduced embryo length of Δ54U8-3 mutants, whereas LCC mutants specific to the 3′ extension restore Δ54U8-3 mutant embryo length to that of wild-type siblings. n = 4–8 embryos per genotype. Blue and black data points represent embryos collected from two different pairs of heterozygote Δ54U8-3 adults. Error bars indicate SD from the mean.