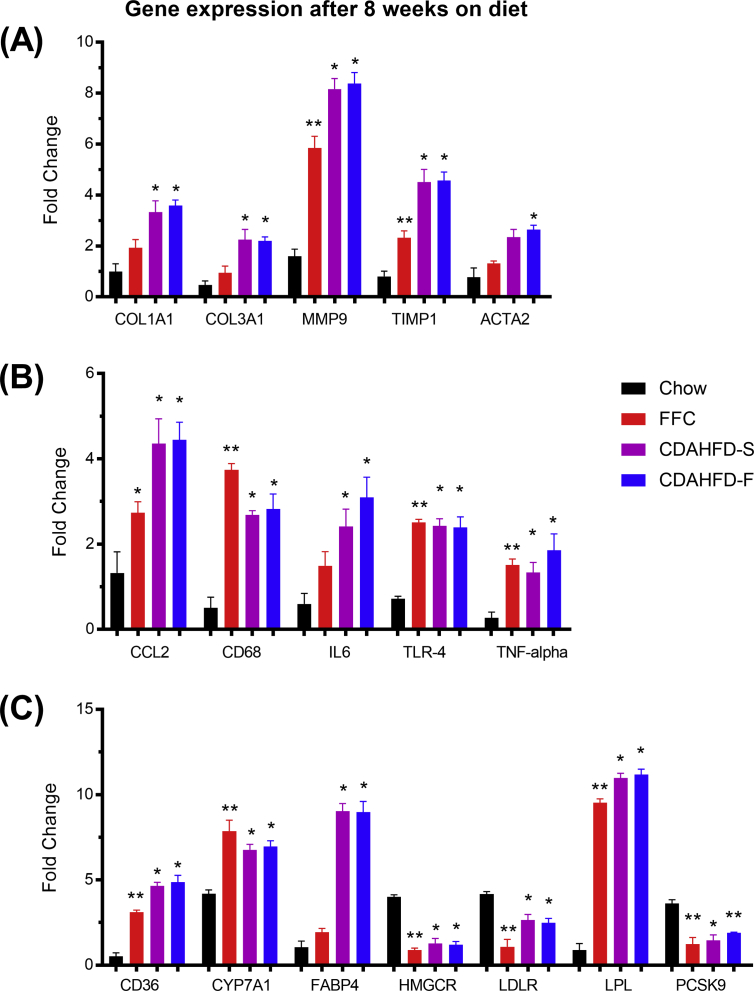
Figure 6.
Hepatic mRNA levels for genes associated with fibrosis (A), inflammation (B), and lipid metabolism (C) after 8 weeks of feeding Göttingen Minipigs with different diets: chow (n = 5), FFC (n = 5), CDAHFD-S (n = 4), and CDAHFD-F (n = 3). The data were normalized to a panel of four stable reference genes and are represented as means + SEM of the fold changes for each diet group. *P < 0.05 vs chow, **P < 0.01 vs chow. ACTA2, smooth muscle α-2 actin; CCL2, chemokine (C–C motif) ligand 2; CD36, cluster of differentiation (CD) 36; CD68, cluster of differentiation 68; COL1A1, alpha-1 type I collagen; COL3A1, alpha-1 type III collagen; CYP7A1, cytochrome P450 family 7 subfamily A member 1; FABP4, fatty acid–binding protein 4; HMGCR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; IL6, interleukin-6; LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptor; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; MMP9, matrix metalloproteinase-9; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; TIMP1, metalloproteinase inhibitor 1; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; TNFA, tumor necrosis factor alpha; CDAHFD-S, choline-deficient, amino acid–defined high-fat diet with sucrose; CDAHFD-F, choline-deficient, amino acid–defined high-fat diet with fructose; FFC, high fat, fructose, and cholesterol.