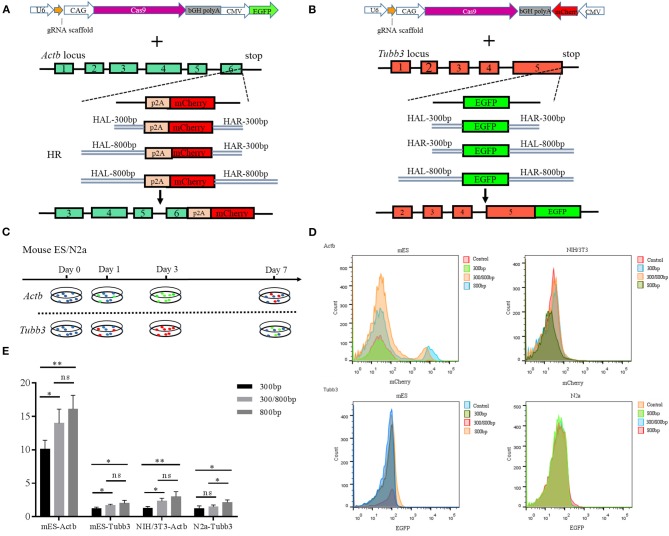
Figure 2.
(A) Schematic overview of the strategy used to target the Actb locus. HAL/HAR, left/right homology arm; HR, homologous recombination; (B) Schematic overview of the strategy used to target the Tubb3 locus; (C) Experimental scheme for targeted knock-in of Actb-p2A-mCherry in mouse ES and NIH/3T3 cells and Tubb3-EGFP in mouse ES and N2a cells. Cells were transfected with donors/GFP or donors/mCherry and Cas9/sgRNA/mCherry/GFP, and transfected cells were sorted based on GFP or mCherry signals 2 days after transfection. (D) Knock-in efficiencies were evaluated by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) and were based on the ratio of GFP+ or mCherry+ cells to all transfected cells; (E) Histograms show relative knock-in efficiencies for different homology arm lengths used for knock-in at Actb and Tubb3 in mouse cells expressed as the percentage of mCherry+ (or GFP+) cells among all transfected cells. Results were presented as mean ± s.d. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ns, no significant difference, unpaired Student's t-test.