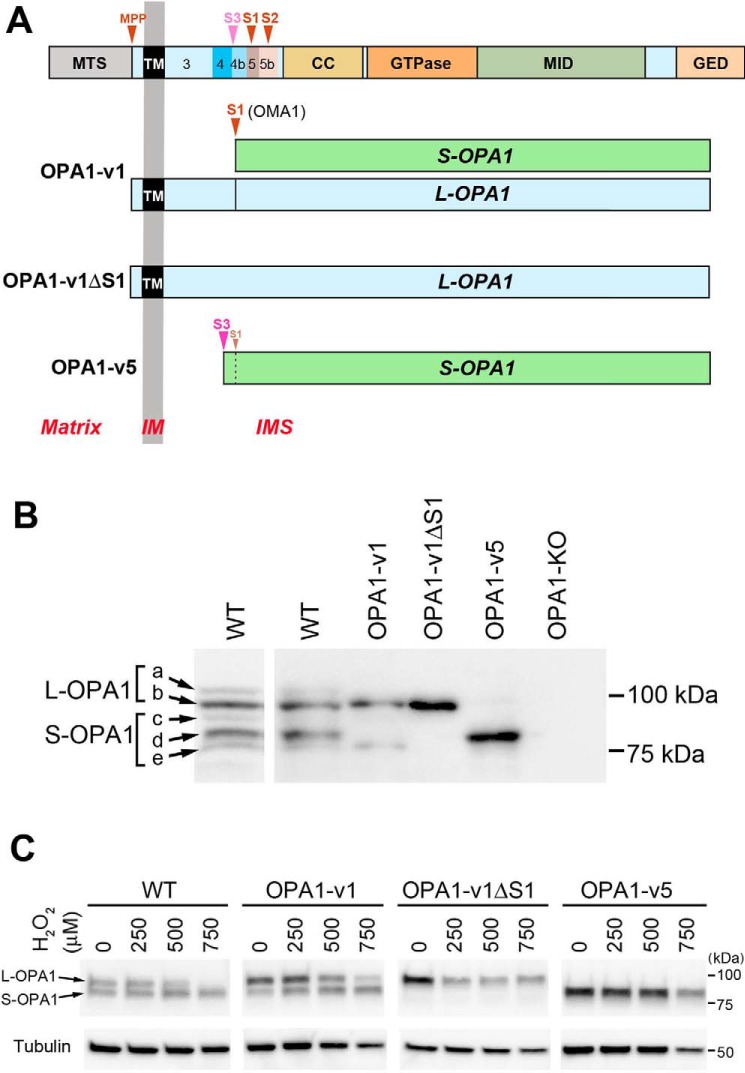
Figure 1.
OPA1 variants used in this study. A, OPA1 protein encoded by all exons is shown at the top. MTS, mitochondrial transit sequence; CC, coiled coil domain; GTPase, GTPase domain; MID, middle domain; GED, GTPase effector domain; MPP, mitochondrial processing peptidase, S1–S3, proteolytic cleavage sites. Exons 3–5b are indicated. OPA1-v1 contains the S1 site where partial cleavage occurs, producing a small amount of S-OPA1. OPA1-v1ΔS1 has the deletion of the S1 site in OPA1-v1, producing L-OPA1 exclusively. OPA1-v5 generates S-OPA1 exclusively because of full cleavage possibly at the S3 site. B, expression of the OPA1 variants in isolated stable lines. Cell lysates of OPA1-v1, OPA1-v1ΔS1, and OPA1-v5 along with WT and OPA1-KO were immunoblotted with anti-OPA1 antibody. A separate WT immunoblot is included for clarity of different OPA1 bands (a–e). C, OPA1 cleavage in oxidant insult. Cell lysates of WT and the OPA1 variant cells treated with 250, 500, and 750 μm H2O2 for 16 h in OXPHOS media were immunoblotted for OPA1. WT and OPA1-v1 cells show the conversion of L-OPA1 to S-OPA1, most notably in 500 and 750 μm H2O2.