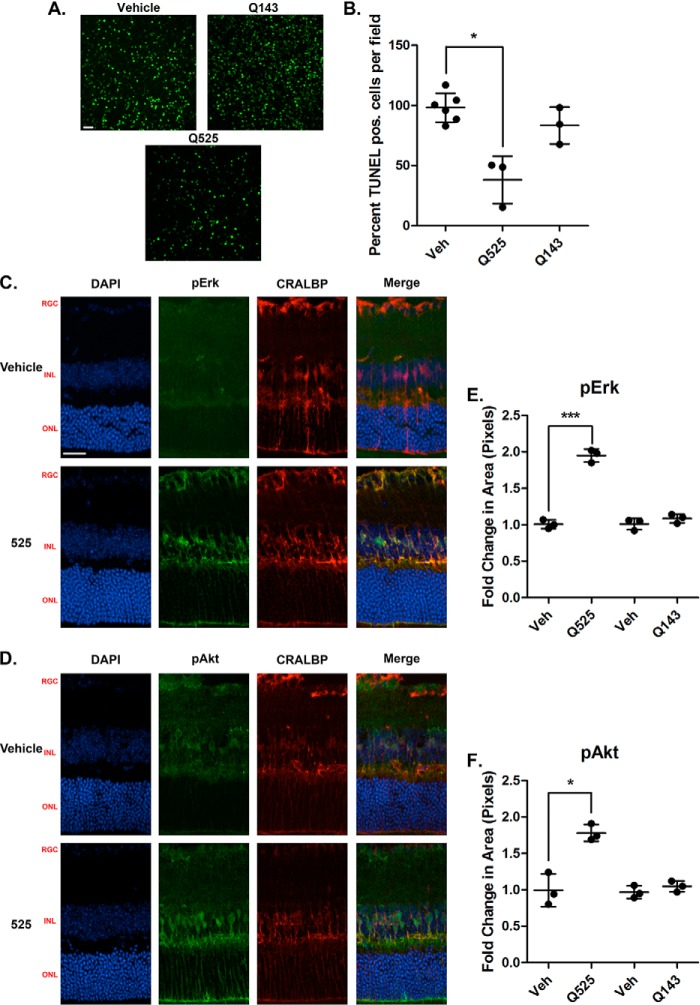
Figure 5.
Q525 is neuroprotective ex vivo in a mouse model of retinal degeneration and activates trophic signals in Muller glial cells. A, representative confocal images of retinal flat mounts following treatment with Q525 and Q143. Freshly dissected retinas from 18-day-old RHOP347S mice were incubated in culture medium for 24 h: one retina with the indicated compounds and the contralateral retina of the same mouse with vehicle control (e.g. each individual had its own internal control). The tissues were processed for TUNEL staining and flat-mounted. 12 images were taken per retina and quantified semiautomatically. B, quantification of TUNEL-positive (pos.) cells after treatment. Cell counts from n = 3 mice/group were standardized versus vehicle control (Veh). Q525 treatment affords a significant reduction in TUNEL staining, whereas Q143 treatment was comparable to vehicle. *, p < 0.05, Student's t test. C and D, images of retinal sections stained for pErk and pAkt following intravitreal injection of compound Q525 in vivo. Eyecups were collected 1 h after injection. Significant increases in staining for pErk and pAkt co-localized with the Muller cell marker CRALBP, suggesting activation within the glial population. RGC, retinal ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer. Scale bar, 25 μm. E, pErk quantification of Q525 and Q143 retinal sections (n = 3/group) expressed as the fold change in pixel area over vehicle ± S.D. ***, p < 0.0005, Student's t test. F, pAkt quantification of Q525 and Q143 retinal sections (n = 3/group) expressed as the fold change in pixel area over vehicle ± S.D., *, p < 0.05, Student's t test. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.