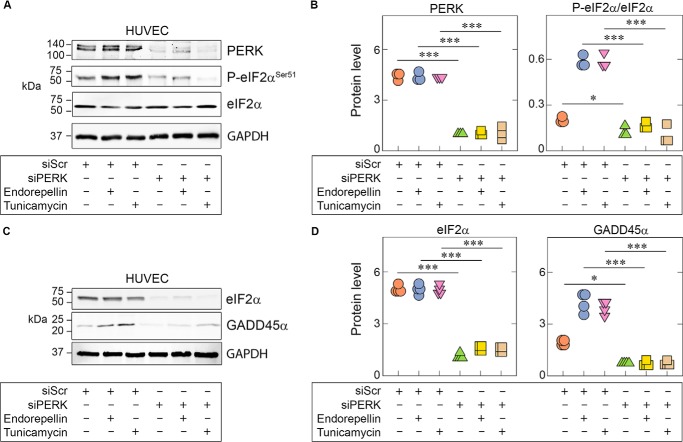
Figure 2.
Endorepellin-dependent PERK and eIF2α activation is essential for downstream GADD45α up-regulation. A, representative immunoblots of HUVECs pretreated with 100 pm scrambled siRNA (siScr) or siRNA targeting PERK (siPERK), followed by treatment with endorepellin (200 nm) or tunicamycin (10 μg/ml). Lysates show RNAi-mediated knockdown of PERK (siPERK) and subsequent suppression of eIF2α phosphorylation. Treatment conditions are indicated in the bottom panel. B, quantification of PERK and p-eIF2α from A, normalized on GAPDH for PERK or total protein level for P-eIF2α. Data are from three independent biological experiments (n = 3). C, representative immunoblots of HUVECs pretreated with 100 pm scrambled siRNA (siScr) or with siRNA targeting eIF2α (sieIF2α), followed by treatment with endorepellin (200 nm) or tunicamycin (10 μg/ml). Lysates show RNAi-mediated knockdown of eIF2α (sieIF2α) and subsequent suppression of GADD45α levels. D, quantification of eIF2α and GADD45α from C, normalized to GAPDH. Data are from three independent experiments (n = 3). Statistical significance was calculated via two-tailed unpaired Student's t test (**, p < 0.01). All statistical analyses were calculated via one-way ANOVA (***, p < 0.001).