Figure 7.
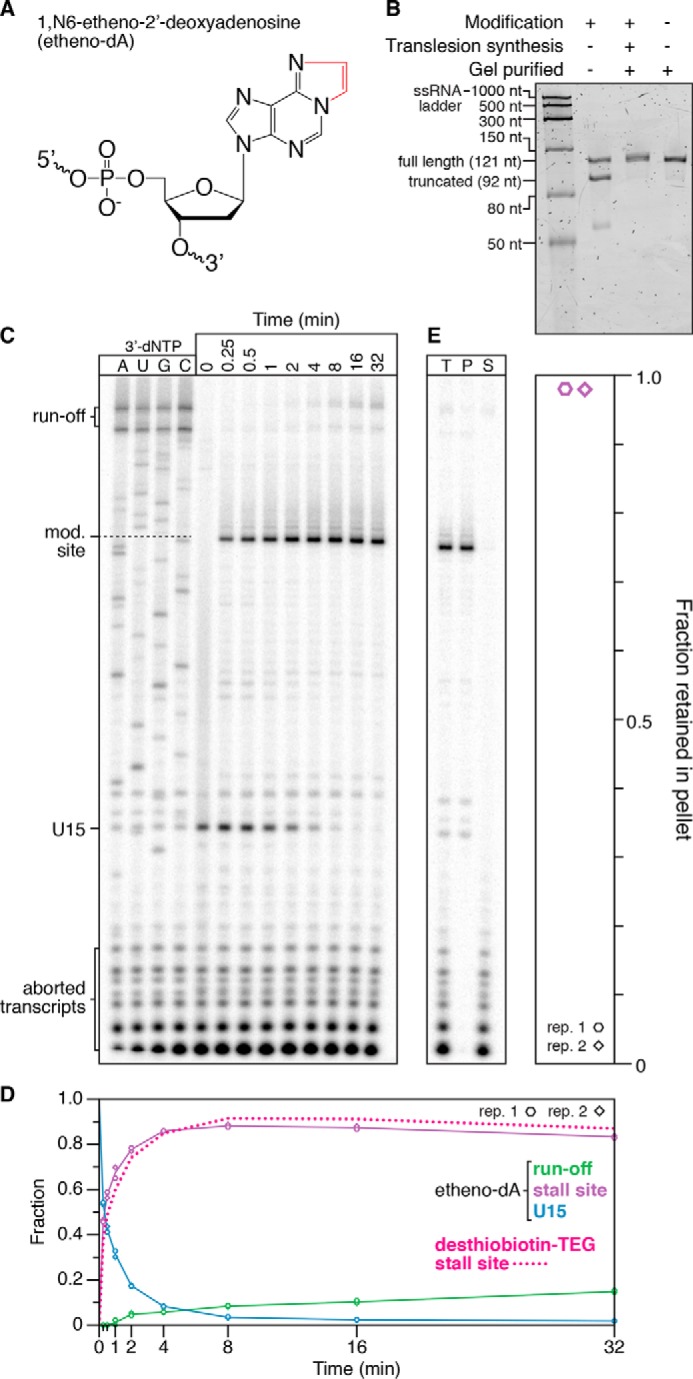
Transcription roadblocking by etheno-dA. A, chemical structure of etheno-dA. The etheno bridge that occludes the adenine Watson–Crick face is highlighted in red. B, denaturing PAGE quality analysis of an internal etheno-dA–modified DNA template preparation (Modification +) alongside an unmodified (Modification −) positive control. The size marker is the Low Range ssRNA Ladder (New England Biolabs). C, single-round in vitro transcription of an internal etheno-dA–modified DNA template in the presence of 500 μm NTPs. RNAP stalls one nucleotide upstream of the modification (mod.) site. D, quantification of the gel shown in C. The decay of TECs stalled at a desthiobiotin–TEG modification is shown for comparison and is from Fig. 3. E, fractionation of TECs stalled at an etheno-dA modification site using streptavidin-coated magnetic beads. DNA templates were attached to streptavidin-coated magnetic beads by a 5′-biotin–TEG modification upstream of the promoter. T, P, and S fractions are shown. The plot shows the fraction of TECs retained in the bead pellet. All data are from two independent replicates. A comparison of DNA template preparation replicates is shown in Fig. S3.
