Figure 3.
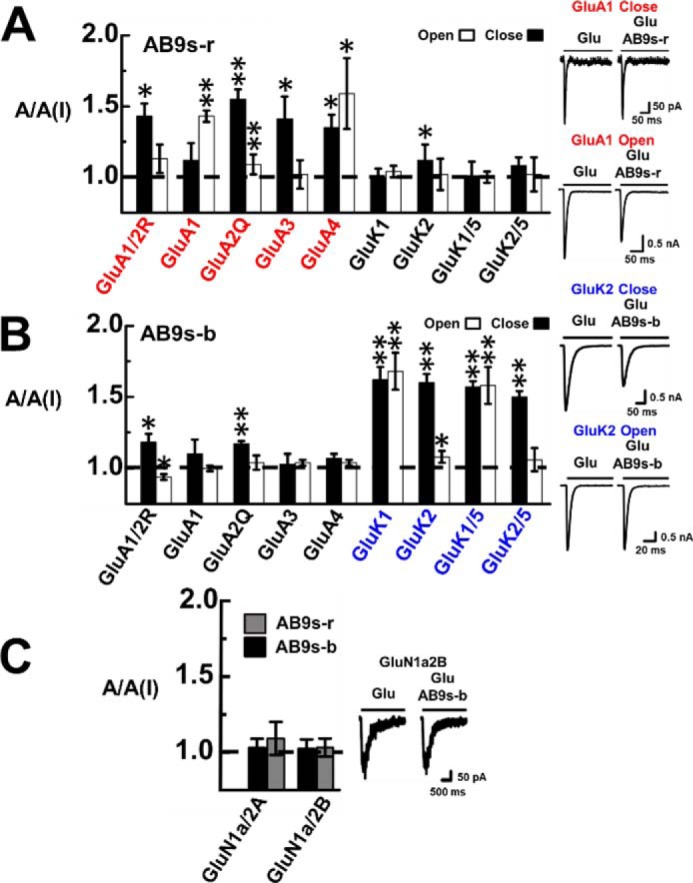
Selective inhibition of glutamate receptor subunits by AB9s-r and AB9s-b. The inhibition is represented by the A/A(I) ratio or the ratio of whole-cell current amplitude in the absence, A, and the presence of 2 μm aptamer, A(I). For each of the receptor subunits and types, the glutamate concentration was chosen to be equivalent to ∼4% and ∼95% fraction of the open channels. Specifically, the glutamate concentration was 0.05 mm for the closed-channel form and 3 mm for the open-channel form for GluA1/2R and GluA1, 0.5 and 10 mm for GluA3, and 0.1 and 3 mm for GluA4. The kainate receptors were tested at 0.05 mm glutamate for closed-channel and 3 mm for the open-channel forms. The difference between open- and closed-channel states was determined with a two-sample, two-tailed Student's t test. Error bars indicate standard deviation from the mean, and all results are based on at least three measurements. A, AB9s-r shows preferential inhibition toward AMPA receptor subunits (red labels) over kainate receptor subunits. Shown on the right are representative whole-cell current responses of GluA1 to glutamate in the absence and presence of aptamer AB9s-r. At the low glutamate concentration, the kdes values of GluA1 in the presence and absence of the aptamer were estimated to be 131 ± 9 and 127 ± 8 s−1, respectively. At high glutamate concentration, the kdes values with and without the aptamer are 166 ± 8 and 160 ± 8 s−1, respectively. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey HSD test analysis comparing closed-channel and the open-channel AMPA and kainate A/A(I) values shows p levels of 0.00042 and 0.06310, respectively. B, AB9s-b shows preferential inhibition toward kainate receptor subunits (blue labels) over AMPA receptors. Also shown on the right is a pair of representative whole-cell current responses of GluK2 to glutamate in the absence and presence of aptamer AB9s-b. At low glutamate concentration, kdes values of 40 ± 2 and 38 ± 4 s−1 were determined for GluK2 with and without the aptamer. At high glutamate concentration, we found kdes to be 226 ± 7 and 214 ± 13 s−1 with and without AB9s-b. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey HSD test analysis comparing closed-channel AMPA and kainate A/A(I) values has p < 0.00001. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey HSD test analysis comparing the open-channel AMPA and kainate A/A(I) values resulted in p = 0.00036. C, the specificity against NMDA channels was tested at a concentration of 5 μm glutamate for GluN1a/2B and 50 μm glutamate for GluN1a/2A. Neither AB9s-r (gray columns) nor AB9s-b (black columns) significantly inhibited the NMDA channels, as seen in the pair of representative whole-cell current response of GluN1a2B in the absence and presence of AB9s-b. From these traces, we estimated the kdes values to be 4 ± 0.3 and 4 ± 0.4 s−1, respectively, with and without AB9s-b.
