Figure 2.
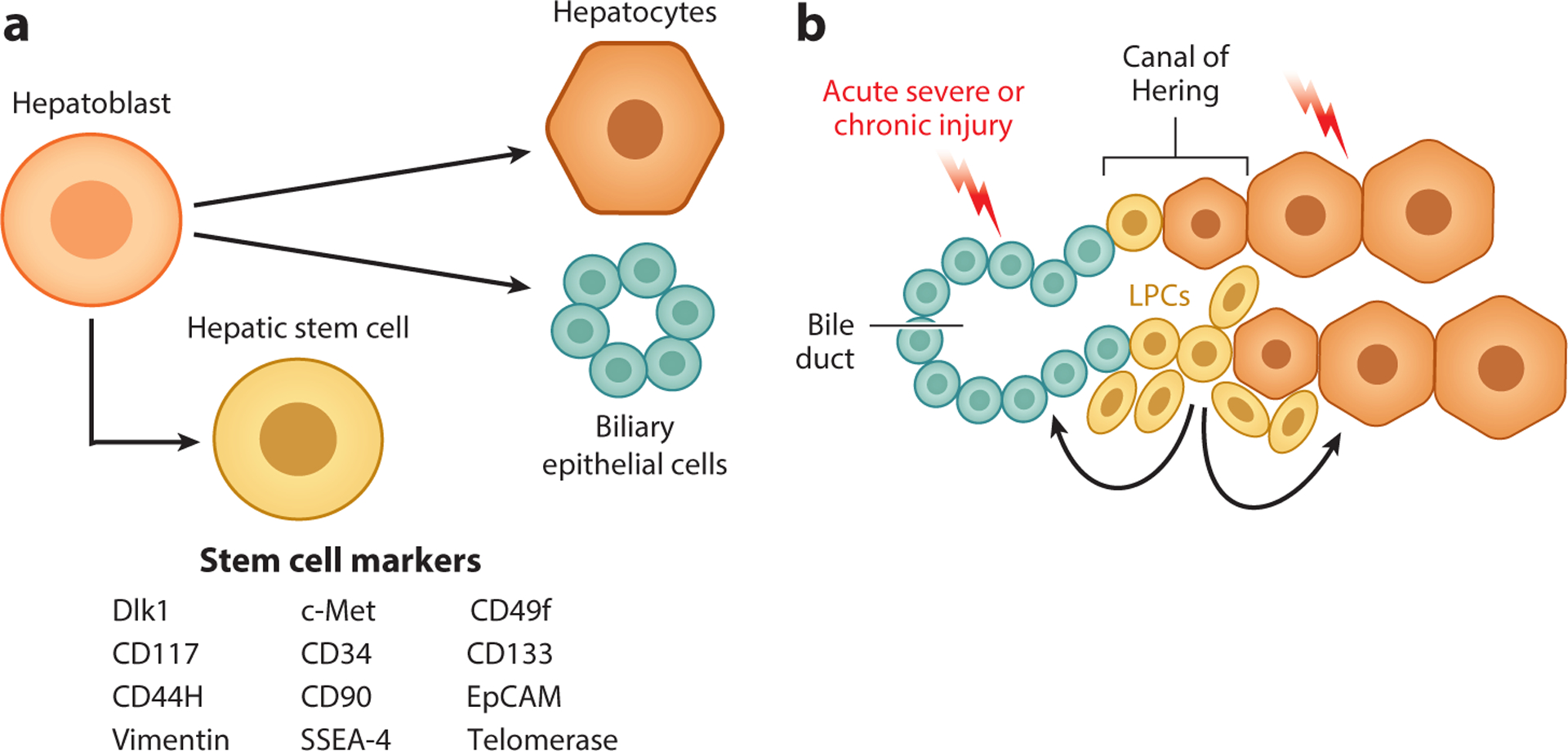
The liver progenitor cell theory. (a) During fetal liver development, hepatoblasts give rise to the two primary epithelial cell types of the mature liver: hepatocytes and biliary epithelial cells. Studies have identified potential markers of hepatoblasts with characteristics of pluripotent stem cells (shown in the figure). (b) It is theorized that quiescent liver progenitor cells (LPCs), potentially residing in the canals of Hering, are activated in the context of severe acute injury or chronic liver injury. These LPCs proliferate and are capable of giving rise to both hepatocytes and cholangiocytes, thus contributing to liver repair.
