Figure 1: Tangential flow analyte capture (TFAC) technique for isolation of particles.
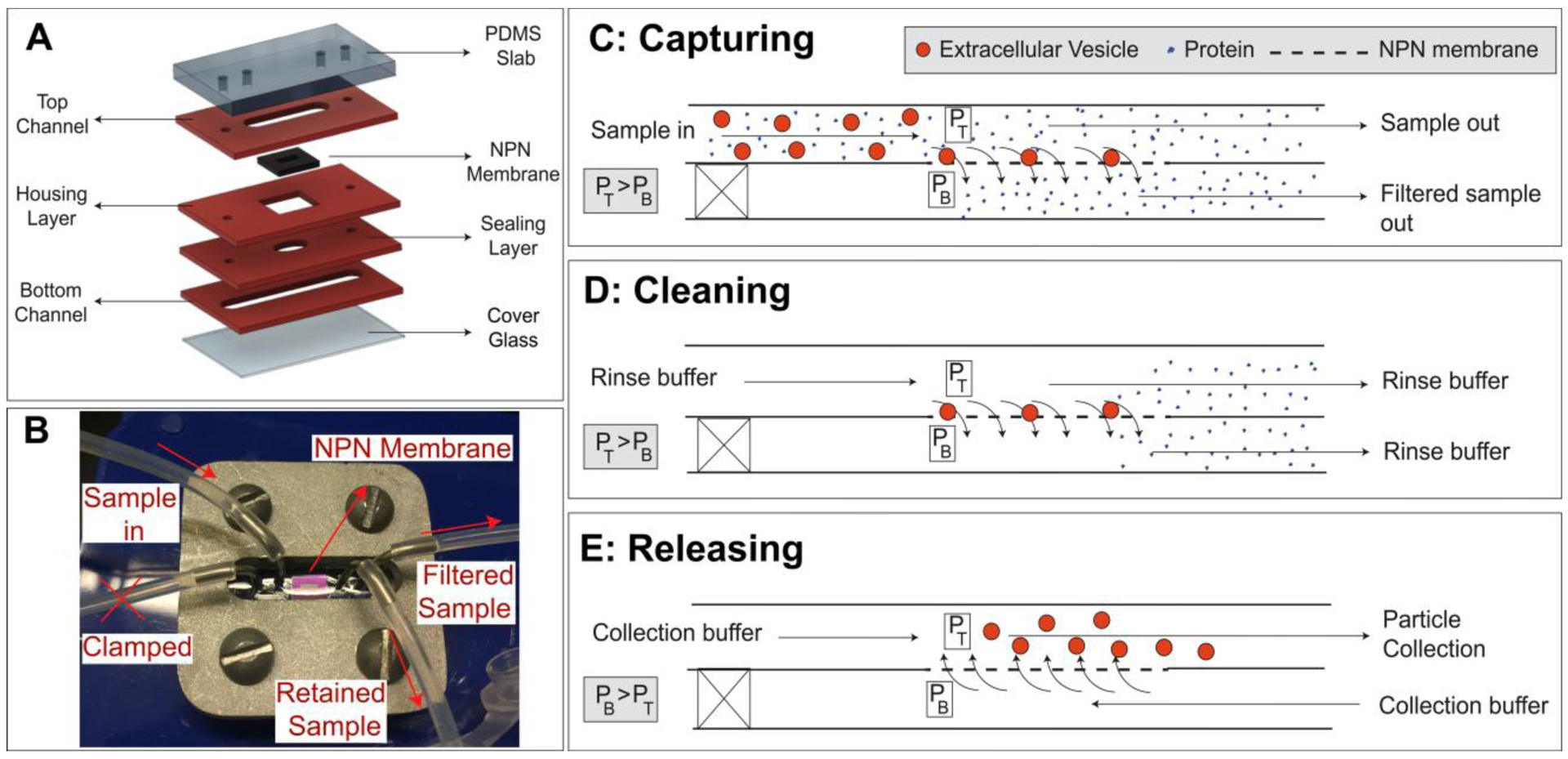
A) Microfluidic devices are assembled through a layer stack process, in which channels and other featured are patterned into PDMS sheets. B) These layers are then formed into the device through thermal bonding or stacking and clamping. C) The sample is passed across the surface of the membrane and a transmembrane pressure generated by syringe pumps drives particle motion towards the membrane. Contaminating particles pass through pores or are swept downstream while the particles are retained on the membrane surface. D) The cleaning buffer is then passed through the input channel under the same flow condition as the capturing step to wash the channel and membrane surfaces of any remaining contaminants. E) The transmembrane pressure is then reversed, releasing the particles from the membrane where they are then swept downstream and collected.
