Fig. 4. The m6A level of carRNAs affects local chromatin state and downstream transcription.
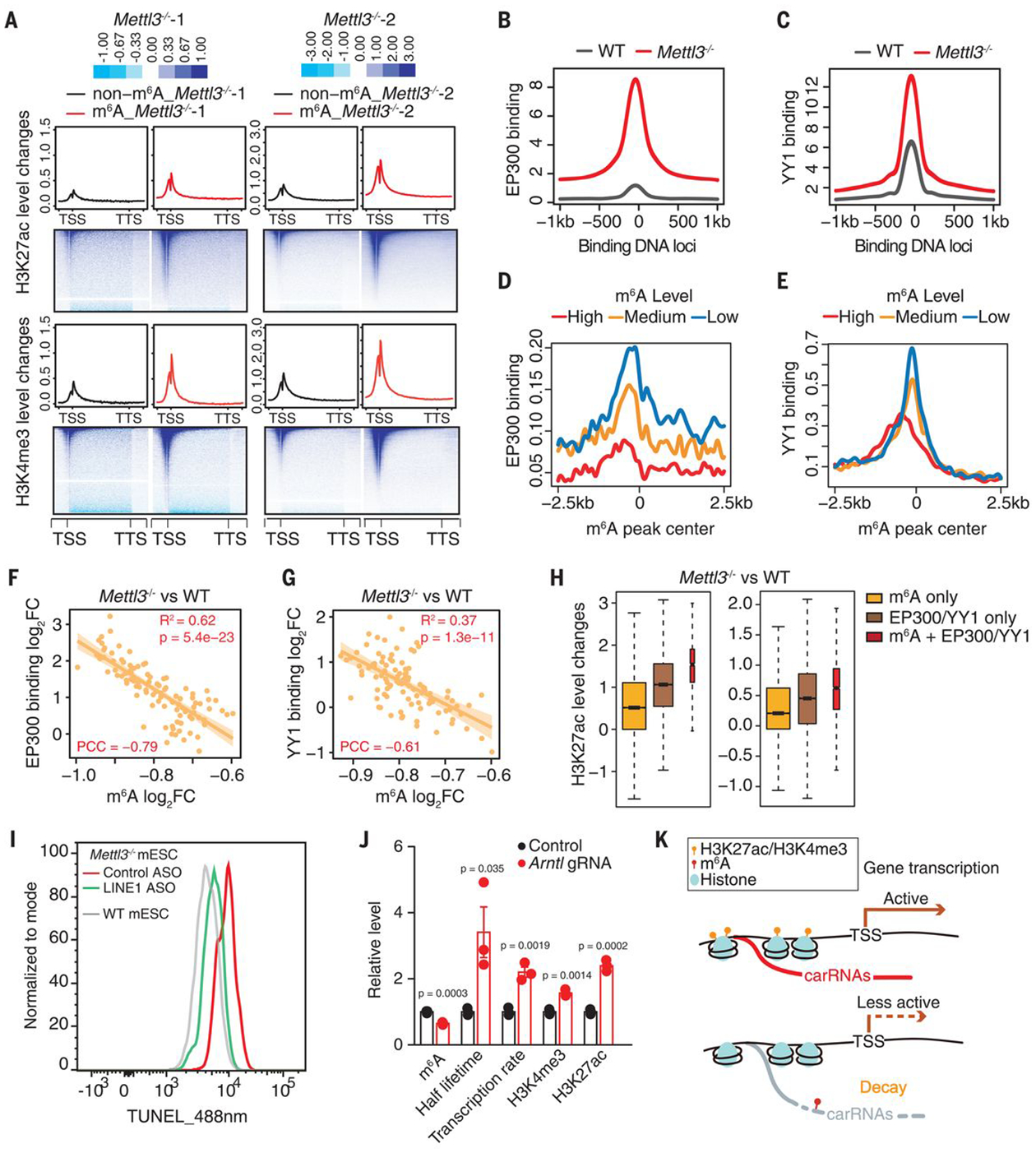
(A) Profiles of H3K27ac (top) and H3K4me3 (bottom) level changes on gene body together with 2.5 kb upstream of the TSS (transcription start site) and 2.5 kb downstream of the TTS (transcription termination site) in WT and Mettl3 KO mESCs. Genes were categorized into two groups according to whether they harbor upstream m6A-marked carRNAs (m6A) or not (non-m6A). (B and C) Profiles of EP300 (B) or YY1 (C) DNA binding at their peak center and flanking 2.5 kb regions in WT and Mettl3 KO mESCs. (D and E) Profiles of EP300 (D) and YY1 (E) DNA binding at the center of m6A peaks overlapped with carRNAs and its flanking 2.5 kb regions in WT mESCs. m6A peaks were categorized into highly (high), moderately (medium), or lowly (low) methylated groups, according to their m6A levels in WT mESCs. (F and G) The correlation between changes in m6A level of the carRNAs and changes in EP300 (F) or YY1 (G) DNA binding at genomic regions that show m6A differences with Mettl3 KO. The genomic regions were categorized into 100 bins on the basis of fold change rank of m6A level upon Mettl3 KO. (H) Barplots showing H3K27ac level changes at genomic regions that are m6A methylated (m6A only, without EP300 and YY1 binding), bound by EP300 or YY1 (EP300/YY1 only, without m6A carRNA), and m6A methylated with EP300 and YY1 binding (m6A + EP300/YY1). The last group showed the highest increase upon Mettl3 KO. (I) Analysis of chromatin accessibility in Mettl3 KO mESCs treated with control or LINE1 antisense oligos (ASOs). DNase I–treated TUNEL assay was performed. (J) A dCas13b-FTO (WT or inactive mutant) construct with gRNA targeting the seRNA of Arntl was used to reduce the m6A level of Arntl seRNA. After treatment, increased half lifetime of the target seRNA, elevated local H3K27ac and H3K4me3 levels, and increased Arntl transcription rate were observed, accompanied by the decreased seRNA m6A level. (K) A schematic model showing how m6A affects transcription by regulating the decay of upstream carRNAs stability and chromatin state.
