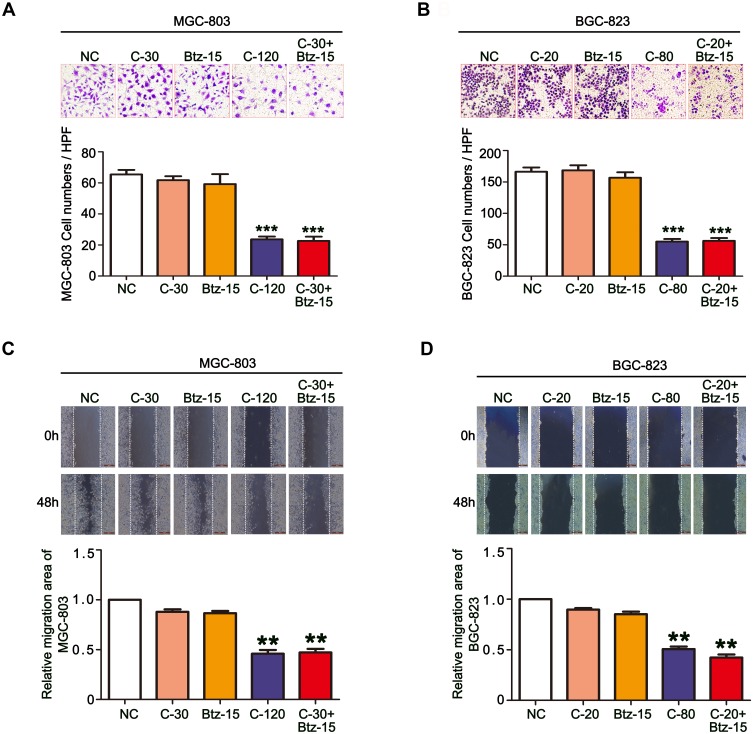
Figure 4.
The combination of chidamide and bortezomib synergistically inhibited the migratory abilities of MGC-803 and BGC-823 cells. The MGC-803 and BGC-823 cell lines were treated with chidamide (30 µM for MGC-803 or 20 µM for BGC-823), bortezomib (15 nM), chidamide (120 µM for MGC-803 or 80 µM for BGC-823), or chidamide (30 µM for MGC-803 or 20 µM for BGC-823) in combination with bortezomib (15 nM) for 48 hours. (A and B) Representative images of the Transwell assay results at 24 hours after the different treatments (magnification ×100). Migrated cells were quantified on the basis of the average of four randomly chosen high-power fields from the independent experiments performed in duplicate (One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s posthoc test was applied to compare the indicated groups. ***P<0.001, compared with the negative control, chidamide-, or bortezomib-alone groups). (C and D) Representative images and statistics of cell migration at 24 hours after scratching. Confluent MGC-803 and BGC-823 cell monolayers were wounded by scratching at 48 hours after the different treatments. Cell migration was monitored at 24 hours after wounding (the dotted line indicates the wound edge). The mean area migrated by the MGC-803 and BGC-823 cells was quantified (average of four independent microscope fields from three independent experiments each; One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s posthoc test was applied to compare the indicated groups. **P<0.01, compared with the negative control, chidamide-, or bortezomib-alone groups).