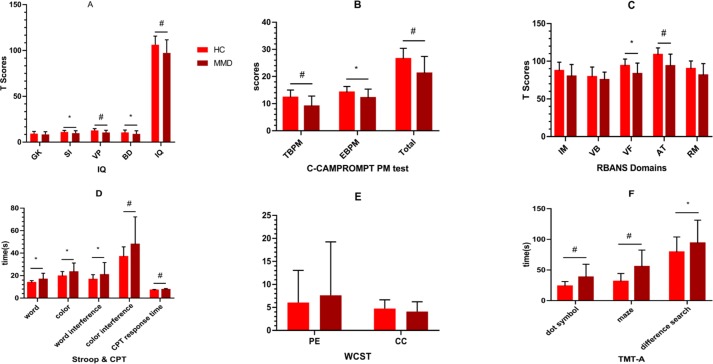
Figure 2.
Comparison of cognitive function between MMD and healthy controls. Compared with the healthy controls matched by gender, age and education time, the adult MMD had a wide range of cognitive impairment, including IQ, PM (both TBPM and EBPM), VF, AT, time dimension of Stroop, CPT and TMT-A. Details may be found in online supplementary material table 4. *, p<0.05; #, p<0.01. AT, attention; BD, block design; C-CAMPROMPT, Cambridge Prospective Memory Test; CC, category completed; CPT, Continuous Persistence Test; EBPM, event-based prospective memory; GK, general knowledge; HC, healthy control; IM, immediate memory; MMD, moyamoya disease; PE, perseverative error; PM, prospective memory; RBANS, Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status; RM retrospective memory; SI, similarity; TBPM, time-based prospective memory; TMT-A, Trail-Making Test Part A; VB, visual breadth; VF, verbal fluency; VP, visual puzzle; WCST, Wisconsin Card Classification Test.