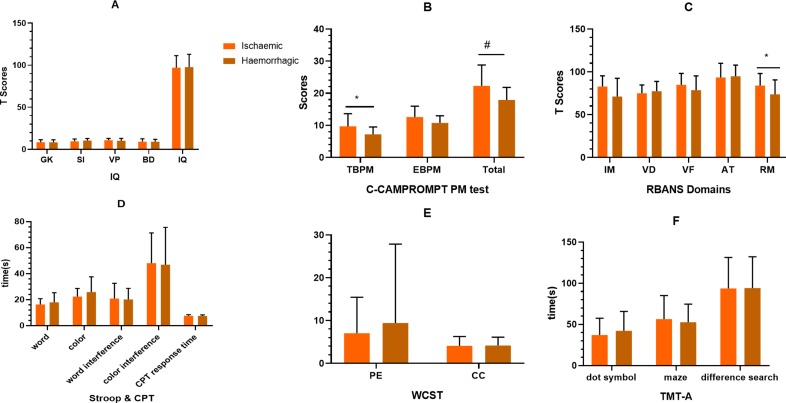
Figure 5.
Comparison of cognitive function between ischaemic and haemorrhagic adult patients with moyamoya disease. The ischaemic patients performed better than the haemorrhagic patients, where the differences in the dimensions of EBPM and RM could be observed. The other dimensions were not significant (p>0.05). Details could be found in online supplementary material table 5. *, p<0.05; #, p<0.01. AT, attention; BD, block design; BPM, event-based prospective memory; C-CAMPROMPT, Cambridge Prospective Memory Test; CC, category completed; CPT, Continuous PersistenceTest; GK, general knowledge; IM, immediate memory; PE, perseverative error; PM prospective memory; RBANS, Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status; RM, retrospective memory; SI, similarity; TBPM, time-based prospective memory; TMT-A, Trail-Making Test Part A; VB, visual breadth; VF, verbal fluency; VP, visual puzzle; WCST, Wisconsin Card Classification Test.