FIGURE 1.
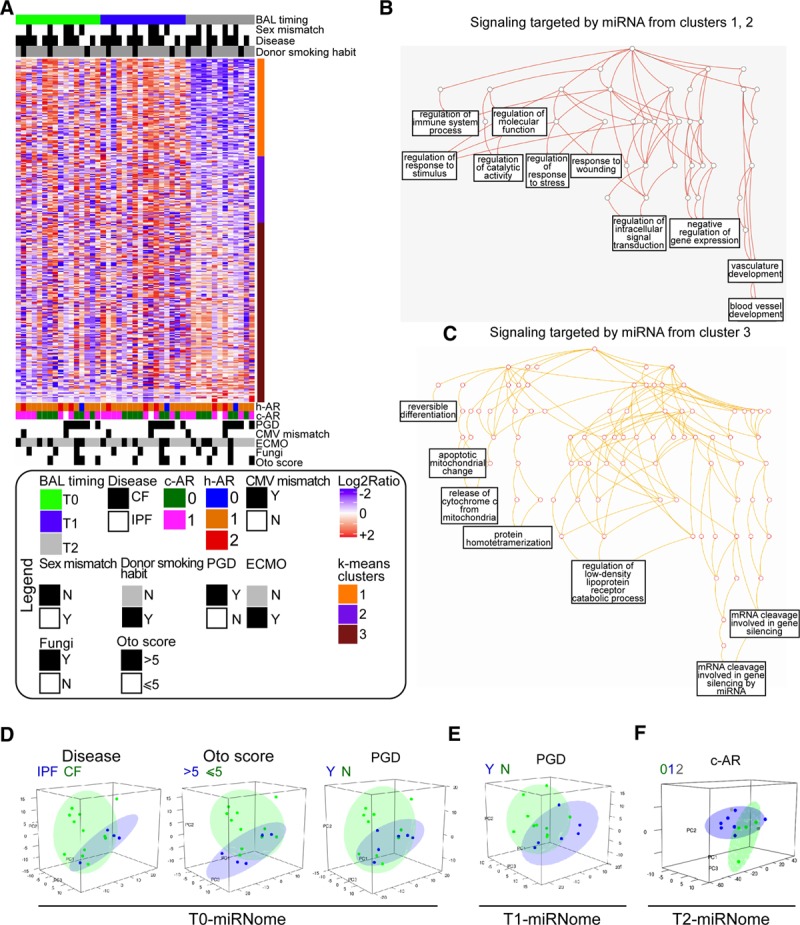
Exploratory analysis of the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)-miRNome in lung transplantation (LTx) patients. A, Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of all BAL-microRNAs (miRNAs) (n = 317) detected in lung-transplanted patients (study phase I, n = 16). BAL samples were collected 7 d (T0), 15 d (T1), or 3 mo (T2) after transplantation. The heatmap shows miRNA levels in all patients at the indicated times. Red and blue indicate high and low expression, respectively. To identify groups of miRNAs with similar behavior, k-means clustering analysis was performed, yielding 3 miRNA clusters (color bar to the right of the heatmap). B and C, Biological processes potentially affected by the top miRNAs in k-means clusters 1 and 2 (B) or cluster 3 (C) target prediction was performed for top miRNAs using the miRTargetLink Human tool, and gene lists were annotated using WebGestalt and GeneOntology as functional database. Significant terms networks are presented as directed acyclic graph (DAG). D–F, Principal component analysis was performed for BAL-miRNAs at T0 (D), T1 (E), and T2 (F) to evaluate the sample distribution according to the indicated clinical variable. The variance explained by the first 3 components was as follows: T0 (PC1: 29%, PC2: 19%, PC3: 11%); T1 (PC1: 33%, PC2: 17%, PC3: 13%); and T2 (PC1: 47%, PC2: 10%, PC3: 9%). c-AR, clinical acute rejection; CF, cystic fibrosis; CMV, cytomegalovirus; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; h-AR, histological acute rejection, grade A; IPF, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; N, no; PC, principal component; PGD, primary graft dysfunction, Y, yes.
