Figure 5. RT-PCR analysis of tight junction protein mRNA expression in IC/PBS cells following treatment with d-proline as-APF or d-pipecolic acid as-APF.
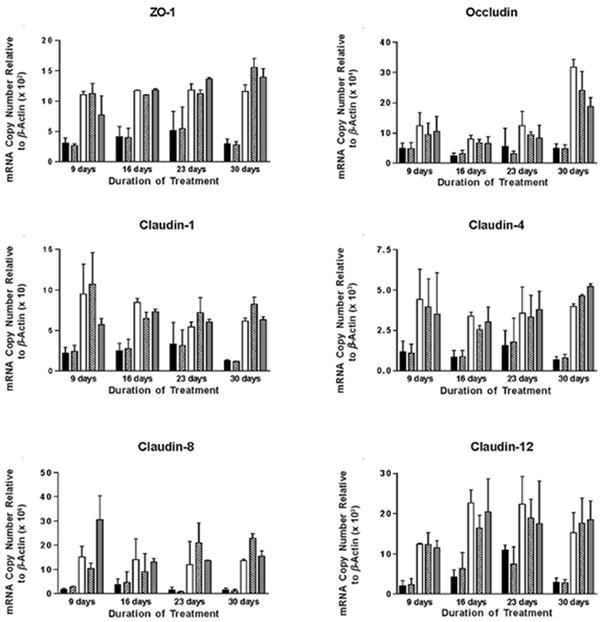
Explanted cells from IC/PBS donors were fed and treated with 2.5 μM d-proline as-APF (□), d-pipecolic acid as-APF (
 ), inactive peptide (
), inactive peptide (
 ), or diluent control (■) twice weekly, and RNA was extracted at 9, 16, 23 and 30 days for qRT-PCR. By day 16, both APF derivatives were able to significantly (p < .05) stimulate tight junction protein expression in IC/PBS cells in vitro resulting in levels similar to those seen in bladder cells from age- and gender-matched normal donors (
), or diluent control (■) twice weekly, and RNA was extracted at 9, 16, 23 and 30 days for qRT-PCR. By day 16, both APF derivatives were able to significantly (p < .05) stimulate tight junction protein expression in IC/PBS cells in vitro resulting in levels similar to those seen in bladder cells from age- and gender-matched normal donors (
 ). PCR was performed in duplicate on three separate occasions for each sample; data are expressed as mean +/- standard error of the mean. (Data shown from experiment with the same IC/PBS cell donor treated simultaneously with either d-pipecolic acid as-APF or d-proline as-APF; d-proline as-APF was tested on cells from a total of 4 IC/PBS donors, with similar results)
). PCR was performed in duplicate on three separate occasions for each sample; data are expressed as mean +/- standard error of the mean. (Data shown from experiment with the same IC/PBS cell donor treated simultaneously with either d-pipecolic acid as-APF or d-proline as-APF; d-proline as-APF was tested on cells from a total of 4 IC/PBS donors, with similar results)
