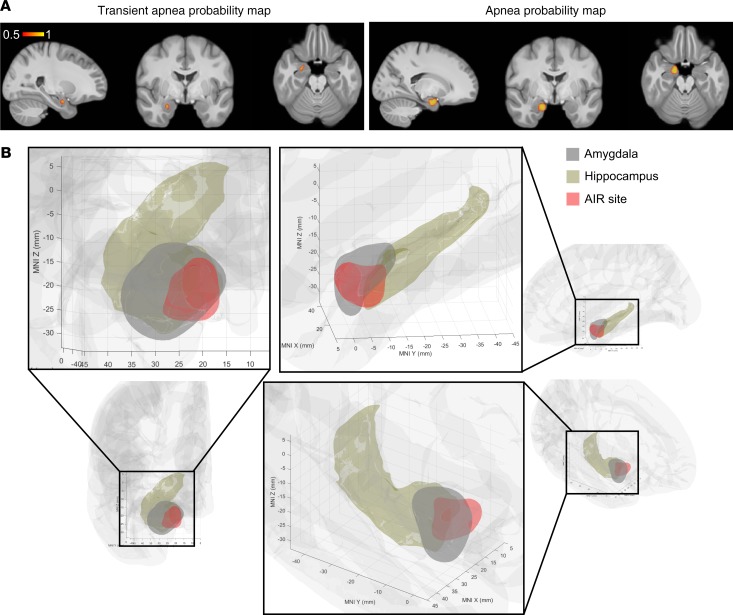
Figure 7. Machine-learning algorithm localizes an amygdala inhibition of respiration site.
(A) Probability map of transient apnea (left) and apnea (right) resulting from support vector machine classification of respiratory effects predicted from MNI coordinates of 45 tested mesial temporal electrode contact pairs. (B) The amygdala inhibition of respiration (AIR) site (red) predicts apnea based on the results of A, overlaid on amygdala (gray, FSL) and hippocampus (brown, FreeSurfer). Probability map is plotted in right hemisphere only for simplicity, because no differences were observed between right and left amygdala stimulation.