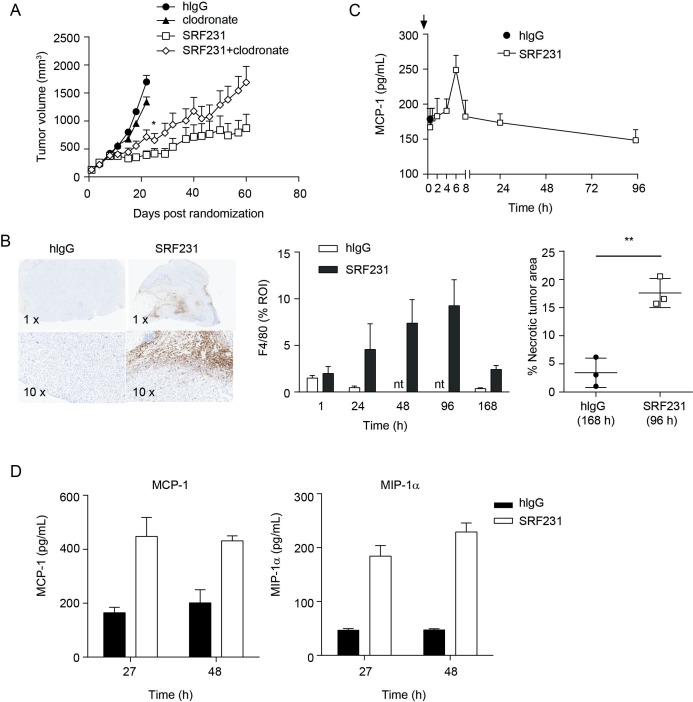
Figure 6.
Macrophages contribute to SRF231 antitumor activity. (A) CB17.SCID mice were inoculated with Raji cells subcutaneously. When tumors reached 100–150 mm3, day 0, mice (n=10/group) were treated with 100 µg clodronate liposomes IV 3 times/week for 2 weeks. On day 4, mice were treated IP with either 100 µg isotype control antibody (hIgG) or SRF231 IP 3 times/week for 3 weeks. Data are shown as mean tumor volumes±SEM; p=0.0451 for SRF231 vs SRF231+clodronate on day 22. (B, C) CB17.SCID mice bearing subcutaneous Raji tumors were treated IP with a single 100 µg dose of hIgG or SRF231. Mice were euthanized and tumors and plasma were collected at 1, 24, 48, 96 and 168 hours after treatments (n=3/group). (B) Representative Raji tumor sections from isotype-treated (168 hours) and SRF231-treated (96 hours) animals were stained with F4/80 (left panel, 1X and 10X magnification). F4/80 percent positive expression (middle panel) and necrotic tumor area percentage (right panel; **p=0.0035) was quantified with digital image analysis software applied to tumor images from both isotype and SRF231-treated animals at the defined timepoints. (C) Plasma MCP-1 expression from Raji tumor-bearing mice at the indicated times following a single 100 µg dose of hIgG or SRF231. (D) HL-60 tumor-bearing mice were treated with a single 100 µg dose of hIgG or SRF231. After 27 and 48 hours, mice (n=5/group) were euthanized, tumors were collected, and tumor lysates were analyzed for expression of mouse MCP-1 (left panel) and MIP1α (right panel). hIgG, human IgG; IV, Intravenous; IP, intraperitoneally; MCP1, Mouse chemoattractant protein 1; MIP1α, macrophage inflammatory protein 1α; nt, not tested; ROI, region of interest.