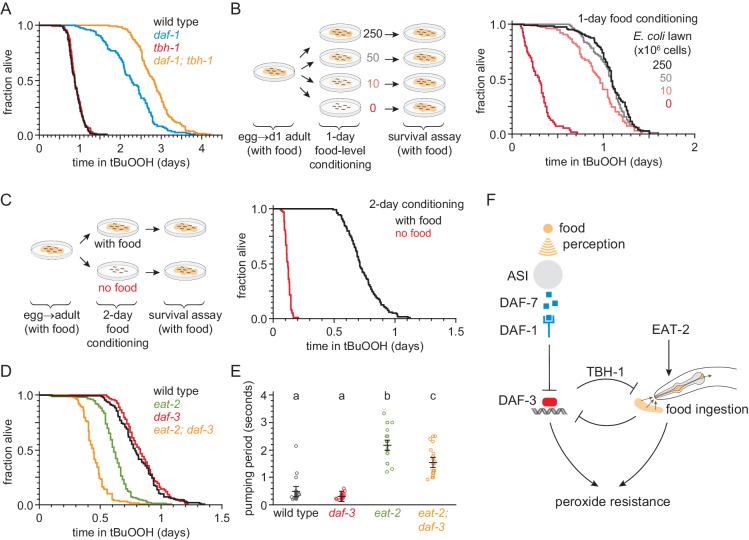
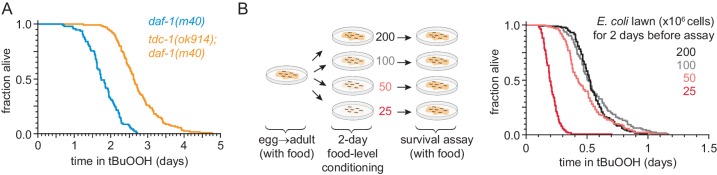
Figure 7. Food ingestion regulates the nematode’s peroxide resistance via DAF-3/coSMAD.
(A) tbh-1(ok1196) increased the peroxide resistance of daf-1(m40). (B–C) The E. coli level before the assay affected C. elegans peroxide resistance in a dose-dependent manner. (D) eat-2(ad1116) caused a more severe reduction in peroxide resistance in daf-3(mgDf90) than in wild type. (E) eat-2(ad1116) caused a less severe reduction in feeding in daf-3(mgDf90) than in wild type. Lines mark the mean pumping period and its 95% confidence interval. Genotypes labeled with different letters exhibited significant differences in pumping period (p < 0.0001, Turkey HSD test) otherwise (p > 0.05). (F) DAF-3 and feeding increase peroxide resistance but attenuate each other’s effects. Feeding inhibits DAF-3; this attenuates the reduction in peroxide resistance caused by reduced feeding. DAF-3 inhibits feeding via TBH-1; this attenuates the increase in peroxide resistance of daf-1 mutants. Sensory perception of E. coli induces DAF-7 expression (Chang et al., 2006; Gallagher et al., 2013) in a concentration-dependent manner (Entchev et al., 2015; Ren et al., 1996) leading to DAF-3 repression by the DAF-7 receptor DAF-1. Therefore, both ingestion and perception of E. coli inhibit DAF-3. See also Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Additional statistical analyses are in Supplementary file 7.