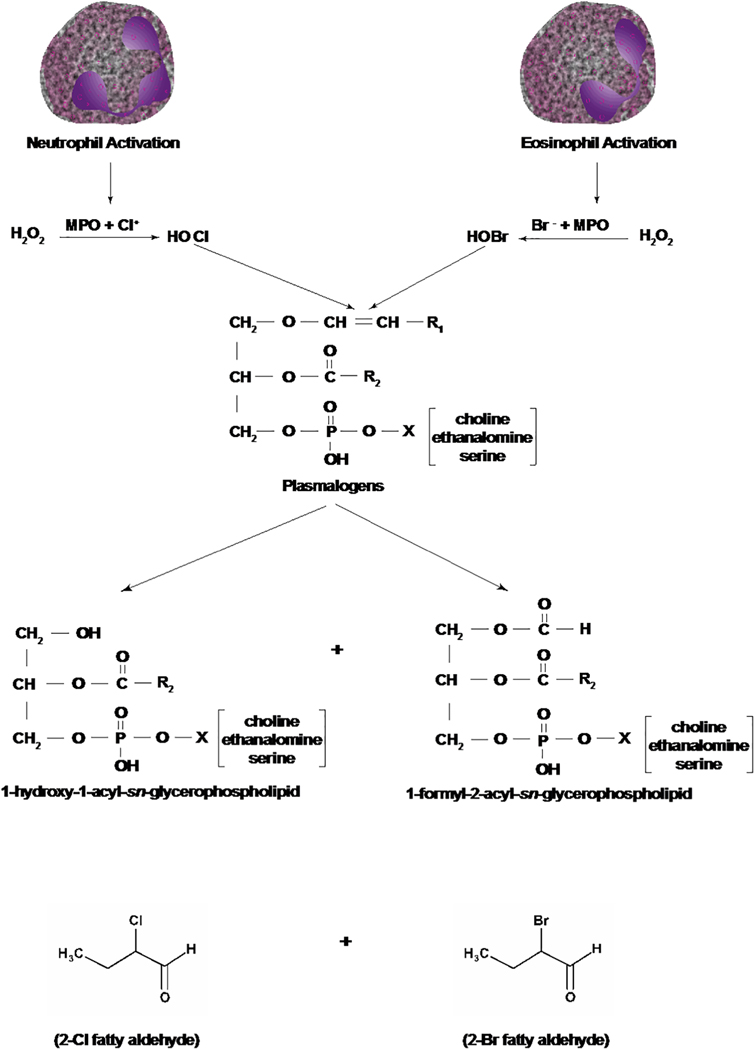
Figure 4: Pathways of generation of 2-chloro- and 2-bromo-fatty aldehydes from plasmalogens by hypochlorous and hypobromous acids.
Activation of neutrophils and eosinophils generates hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and hypobromous acid (HOBr), respectively. HOCl and HOBr by a non-enzymatic mechanism attacks the –CH=CH_ bond of plasmalogens generating 2-chloro- or 2-bromo- fatty aldehydes and 1-hydroxy (lyso)-2-acyl- and 1-formyl-2-acyl-sn-glycerophospholipid where X is choline, ethanolamine or serine. Neutrophil activation releases H2O2, which in the presence of myeloperoxidase (MPO) and chloride ion produces HOCl. Activation of eosinophils releases H2O2 plus eosinophil peroxidase that reacts with bromide ion to form HOBr.