FIGURE 7.
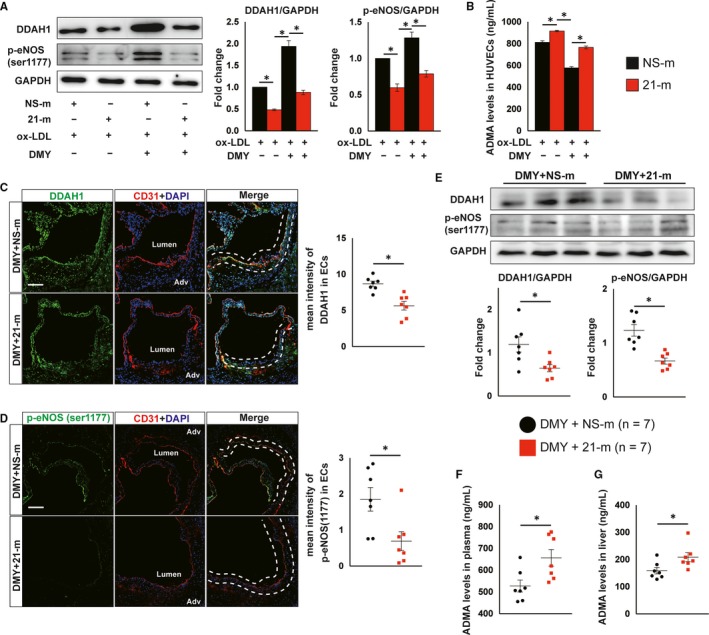
Overexpression of miR‐21 abrogates dihydromyricetin (DMY)‐increased DDAH1 expression and endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase phosphorylation and reduced ADMA levels. HUVECs were transfected with 100 nm agomir NC or miR‐21 agomir for 24 h and then treated with ox‐LDL (120 μg/mL) or ox‐LDL plus DMY (25 μmol/L) for 16 h and harvested for indicated experiments. A Western blot analysis of DDAH1 and p‐endothelial NO synthase (eNOS; ser1177) expression. n = 3 independent experiments. B, ELISA analysis of ADMA levels in cell lysates. n = 3 independent experiment. C, D, Representative images and quantification show DDAH1 (C) and phosphor‐eNOS (ser1177) (D) expression in endothelial cells in the aortic sinus lesions from DMY combined with NS‐m injection or DMY combined with 21‐m injection‐treated Apoe− / − mice fed with HFD for 12 wk. Frozen sections of aortic sinus were stained for anti‐DDAH1 or p‐eNOS (green), anti‐CD31 (red) and DAPI (blue). The dashed line area indicates differential DDAH1 or phosphor‐eNOS expression in endothelial cells. Scale: 50 μm. n = 7 mice per group. E, Western blot analysis of DDAH1 and p‐eNOS (ser1177) expression in liver. n = 7 mice per group. F and G, ELISA analysis of ADMA levels in plasma (F) and livers (G) from DMY combined with NS‐m injection or DMY combined with 21‐m injection‐treated Apoe− / − mice fed with HFD for 12 wk. n = 7 mice per group. Data shown are mean ± SEM. *P < .05
