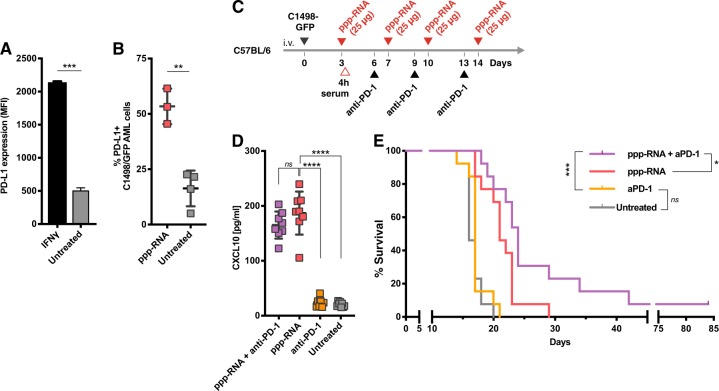
Fig. 5.
ppp-RNA treatment primes AML cells for anti-PD-1 checkpoint inhibition. a 2.5 × 105 C1498-GFP AML cells were seeded in six-well format and treated with interferon gamma. PD-L1 expression was determined by flow cytometry 72 h after stimulation. b C1498-GFP AML-bearing C57BL/6 mice received three treatments of 50 μg ppp-RNA on days 8, 11, and 14 after tumor induction. Twelve hours upon the last treatment (day 15), mice were sacrificed and single cell suspensions of lung tissue were analyzed by flow cytometry, determining PD-L1 expression on GFP+ AML cells. c, d C57BL/6 mice (n = 13 per group derived from two independent experiments) were inoculated with C1498-GFP AML cells on day 0 and treated with 25 μg of ppp-RNA on days 3, 7, 10, and 14. Hundred micrograms of anti-PD-1 antibody was injected i.p. on days 6, 9, and 13. Levels of murine CXCL10 were determined by ELISA in blood serum obtained 4 h after the first treatment with 25 μg of ppp-RNA (n = 8 per group) c. Survival data were plotted in a Kaplan–Meier survival curve (e). Statistical significance was determined by the Student’s t test (a, b), one-way ANOVA with the Tukey’s post-hoc test (c) and the log-rank test (e)