FIGURE 1.
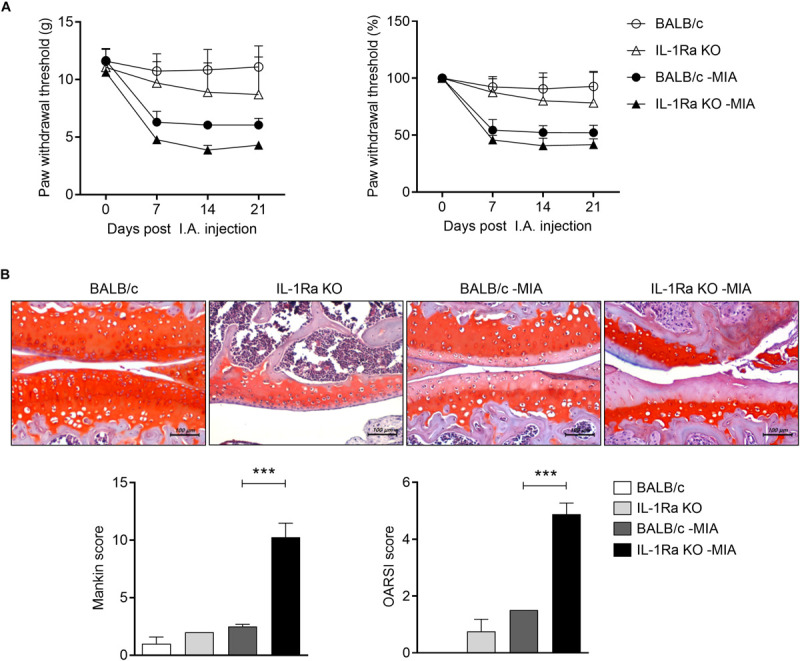
IL-1Ra deficient mice injected with MIA are more sensitive to pain and the treatment promotes articular cartilage damage. (A) BALB/c and IL-1Ra KO mice were injected intra-articularly with 0.6 mg MIA in the right knee. Behavioral tests of secondary tactile allodynia in MIA-injected BALB/c and IL-1Ra KO mice and untreated BALB/c and IL-1Ra KO mice were evaluated using a dynamic plantar esthesiometer (BALB/c n = 5, IL-1Ra KO n = 4, BALB/c MIA n = 4, IL-1Ra KO MIA n = 3). (B) At 3 weeks after the MIA injection, sections of articular tissue from mice were stained with Safranin O and then we evaluated the severity of Mankin and OARSI scores. Representative histological features are shown (original magnification 200×). Three independent experiments were performed. Data are shown as means ± SDs. ***P < 0.001 vs. MIA-injected BALB/c group (One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test).
