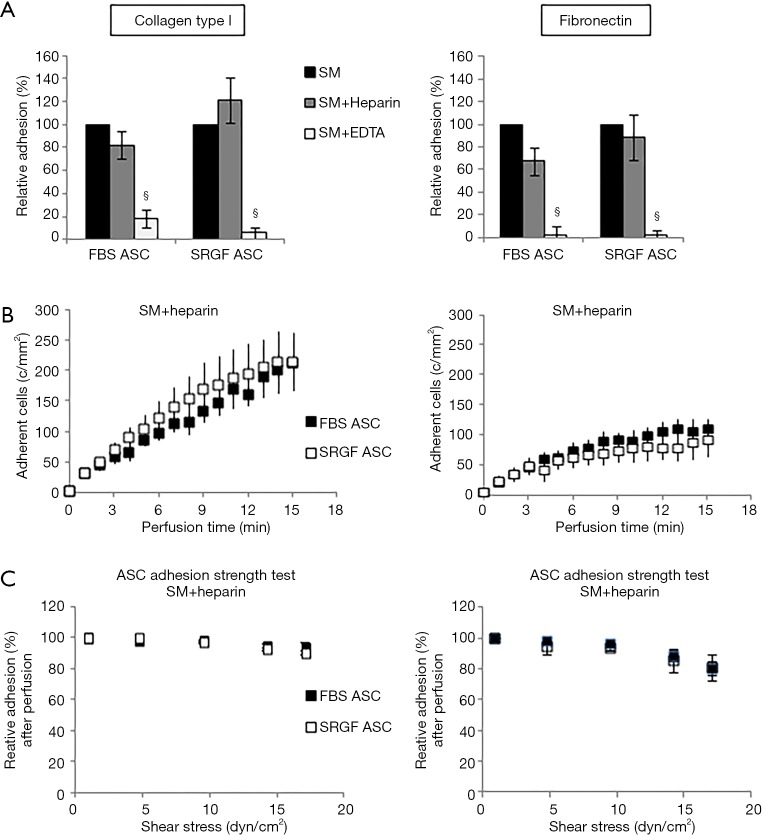
Figure 3.
Impact of heparin and EDTA on ASC adhesion on collagen type I and fibronectin. Impact of heparin and EDTA on FBS and SRGF ASC binding potential (A), kinetics (B) as well as adhesion stability (C) on collagen type I and fibronectin. In (A) density of adherent FBS (248±20 cells/mm2 on collagen type I and 191±15 cells/mm2 on fibronectin) or SRGF (160±24 cells/mm2 on collagen type I and 104±10 cells/mm2 on fibronectin) ASC adhesion in SM (Figure 2B) was considered as 100%; adhesion of FBS or SRGF ASC after addition of heparin and EDTA was expressed as percent (%) relatively to ASC adhesion in SM. In (C) density of adherent FBS or SRGF ASC immediately after perfusion in heparin added SM was expressed as 100% (first dot) and the fraction of adhering FBS or SRGF ASC along with the adhesion strength test was relatively expressed as percent. FBS and SRGF ASC perfusions were performed at 0.1 dyn/cm2. §, P<0.1 versus SM. SM, standard medium i.e., 10% FBS α-MEM medium added with 2% bovine serum albumin; c/mm2, cells/mm2.