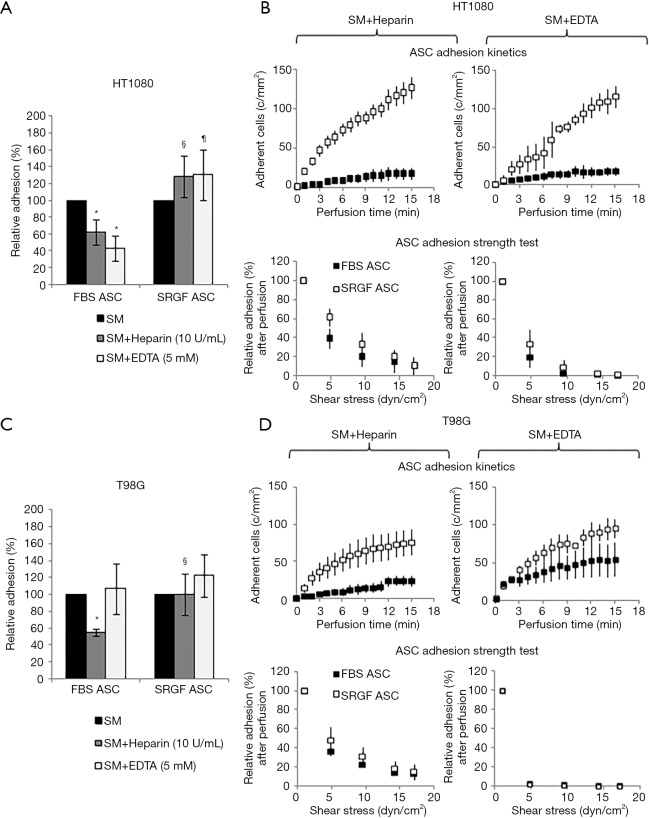
Figure 7.
Impact of heparin and EDTA on ASC adhesion on HT1080, T98G and Huh7. The impact of heparin and EDTA on FBS and SRGF ASC binding potential on HT1080 (A) and T98G (B): the number of adherent FBS (32±7 cells/mm2 on HT1080 and 34±6 cells/mm2 on T98G) and SRGF (81±11 cells/mm2 on HT1080 and 74±4 cells/mm2 on T98G) ASC after perfusion in standard medium on both cellular substrates (Figure 6A) was defined as 100%; adhesion of FBS or SRGF ASC after addition of heparin and EDTA was expressed as percent (%) relatively to ASC adhesion in SM. Moreover, Figure 7 displays the impact of heparin and EDTA on FBS and SRGF ASC kinetics as well as adhesion stability on HT1080 (C) and T98G (D). In ASC adhesion strength test reported in (C) and (D), density of adherent FBS or SRGF ASC immediately after perfusion in heparin or EDTA added SM was expressed as 100% (first dot) and the fraction of adhering FBS or SRGF ASC along with the adhesion strength test was relatively expressed as percent. *, P<0.05 versus FBS ASC perfused in SM; §, P<0.05 vs. FBS ASC perfused in SM + Heparin; ¶, P<0.01 vs. FBS ASC perfused in SM + EDTA; SM, standard medium (10% FBS α-MEM medium added with 2% bovine serum albumin); c/mm2, cells/mm2.