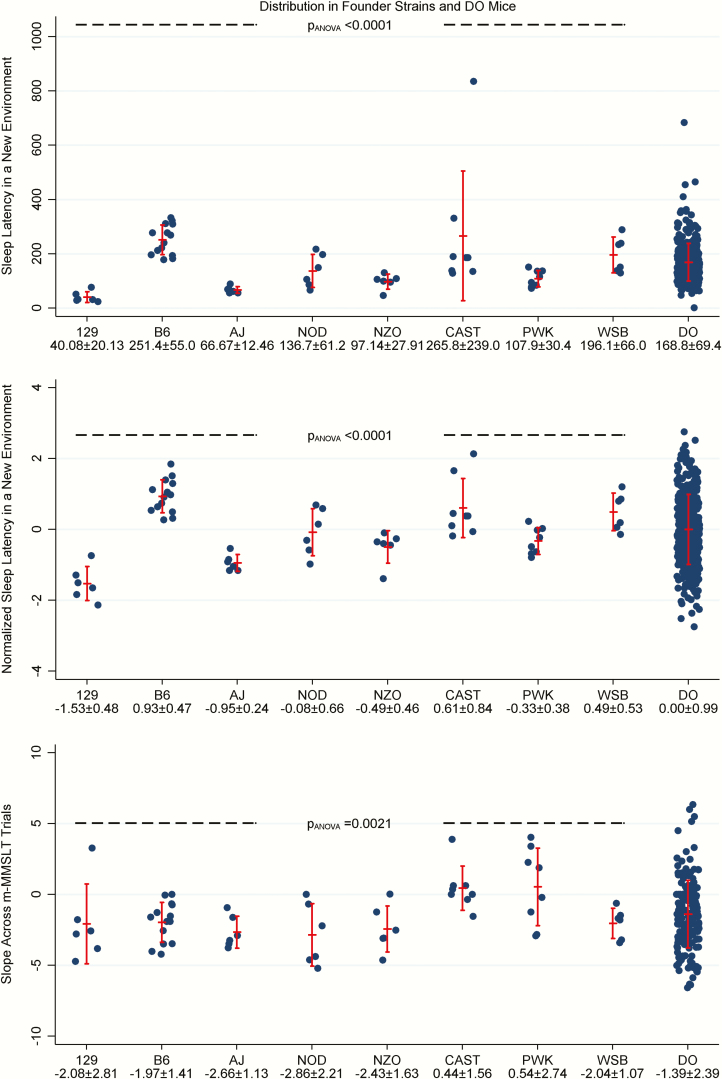
Figure 2.
Sleep latency in a new environment and modified Murine Multiple Sleep Latency Test phenotypes in founder strains and DO mice. Estimates of latency to sleep in a new environment and the slope of latency to sleep across m-MMSLT trials are illustrated within the founder and DO mice. Vertical error bars represent the observed mean ± standard deviation. For sleep latency in a new environment, significant differences were seen among founders (N = 60) on both the observed scale (p = 3.49 × 10−5; top panel) and after rank-based inverse normalization to correct for outliers in the distributions (p = 2.11 × 10−12; middle panel). In general, longer sleep latency is observed for the B6, CAST, and WSB strains, while the shortest sleep latency was seen in the 129 strain. Values in DO mice (N = 338) span the full range seen in the founder strains. We also observed significant differences among the founder strains (N = 60) for the slope of latency to sleep across m-MMSLT trials (p = .0021; bottom panel). In general, the CAST and PWK strain exhibit slope values close to zero (indicating relative resistance to increased sleep deprivation), whereas other founders demonstrated negative slopes (shorter latency to sleep for later trials). We observe broad variability among DO mice (N = 174), with a negative slope on average, but values ranging from −6.59 (indicating high sleep drive) to 6.34 (indicating longer latency to sleep over trials).