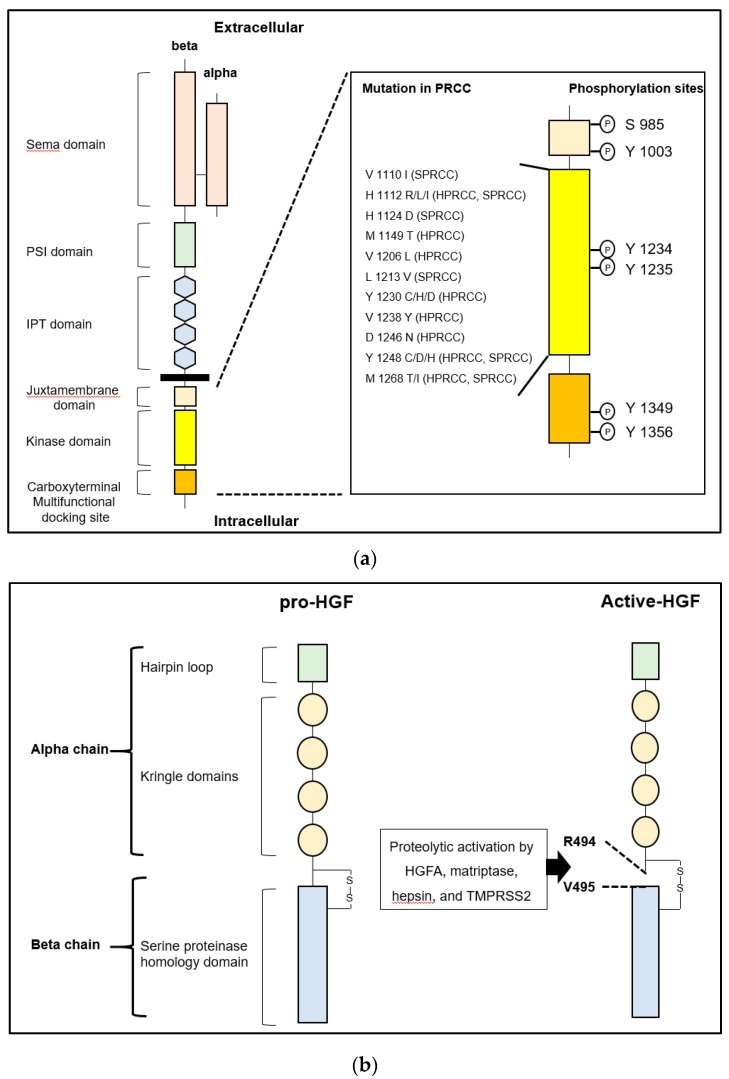
Figure 1.
(a) Left: The structure of human MET is shown. MET consists of extracellular alpha and single-pass transmembrane beta chain, which are disulfide-linked heterodimer. The beta chain is composed of six major domains including Sema (semaphorin), PSI (plexin, semaphorin, integrin), IPT (immunoglobulin-like regions in plexins and transcription factors), juxtamembrane, tyrosine kinase domain, and multifunctional docking site. Right: Sites of point mutation in hereditary and sporadic papillary renal cell carcinoma (HPRCC and SPRCC) and conventional phosphorylation sites in intracellular domains are shown. (b) Left: The structure of human pro-hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is shown. HGF consists of four Kringle domains and a serine proteinase homology domain. Right: The active form of HGF is shown. HGFA, hepsin, matriptase, and TMPRSS2 proteolytically cleave between Arg 494 and Val 495 to convert to a two-chain heterodimeric active form. One-letter abbreviation of amino acids is used.