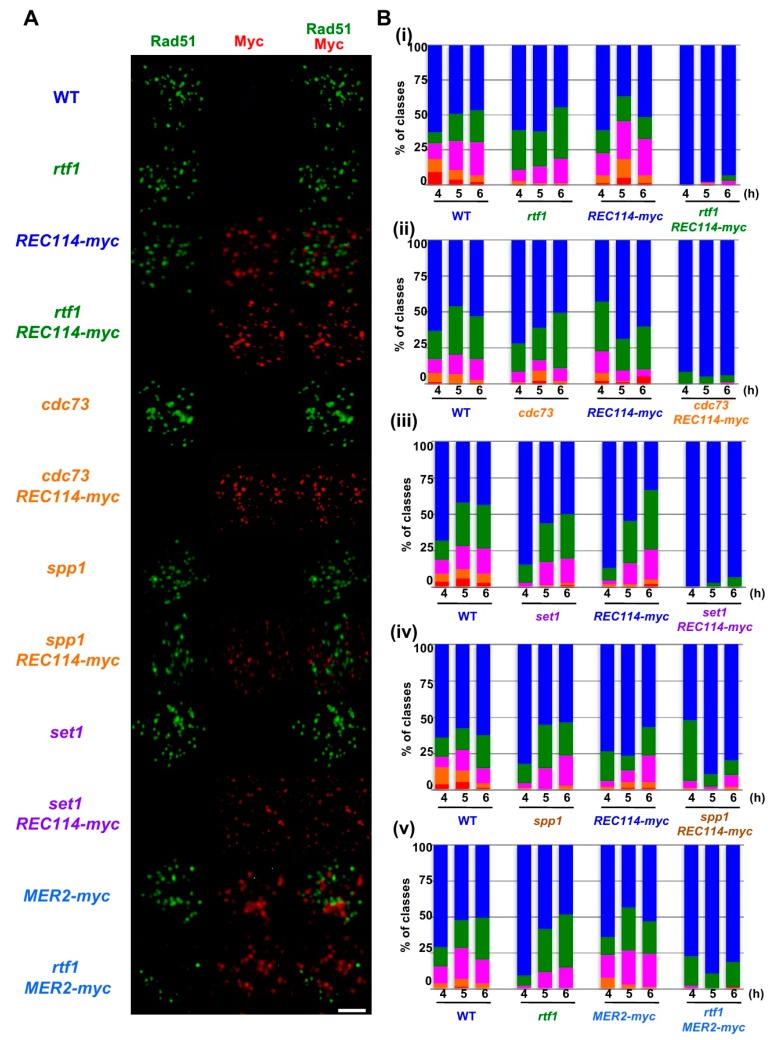
Figure 2.
The REC114-myc showed a synthetic defect in Rad51-foci formation with histone modification mutations. (A) Nuclear spreads from cells undergoing meiosis in various strains were stained with anti-Rad51 (green), anti-myc (red, Rec114/Mer2), and DAPI (blue). The representative images of Rad51/myc/DAPI-staining at 4 h in each strain are shown. Wild type, MSY831/833; rtf1, ZYY839; REC114-myc, ZYY411; rtf1 REC114-myc, ZYY391; cdc73, ZYY811; cdc73 REC114-myc, ZYY736; spp1, ZYY892; spp1 REC114-myc, ZYY739; set1, ZYY733; set1 REC114-myc, ZYY1812; MER2-myc, ZYY893; rtf1 MER2-myc, ZYY874. Bar = 2 μm. (B) The number of Rad51 foci per spread at 4, 5, and 6 h was counted and classified into a spread with less than 5 (Rad51-negative, blue), 6–20 (green), 21–35 (purple), 36–50 (orange), and >50 (red) foci. The graphs show percentages of each class of Rad51-foci numbers. The number is a sum from three independent time courses (n = 126; 42 × 3). Data of wild-type, rtf1, and REC114-myc cells in (i)–(v) were obtained by independent time courses. Statistics for comparison between strains are shown in Table S2.