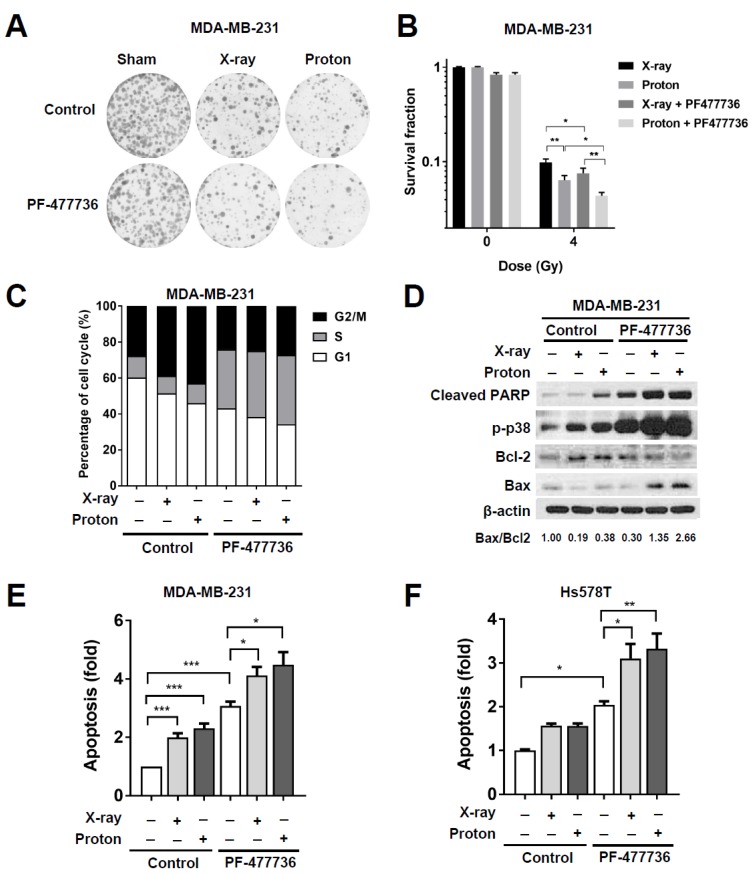
Figure 3.
CHK1 inhibition in response to PF-477736 treatment sensitizes TNBC cells to proton irradiation. (A) Effect of co-treatment with PF-477736 and 4 Gy of X-rays or protons on clonogenic survival. MDA-MB-231 cells were pre-treated with 100 nM PF-477736 for 3 h, followed by irradiation with 4 Gy of X-rays or protons. Colonies were stained with crystal violet after 14 days; (B) Quantification of survived colonies. Data are shown as mean ± S.D. from two independent experiments. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; (C) Cell-cycle distribution after combinatorial treatment with PF-477736 and X-rays or protons. MDA-MB-231 cells pre-treated with 500 nM PF-477746 for 3 h were irradiated with 4 Gy of X-rays or protons and were harvested 24 h after irradiation for flow cytometric analysis. X-ray and proton irradiations led to a significant increase in the cell population at the G2/M phase, and their combination with PF-477736 increased the cell population at the S phase; (D) Western blotting showed that pre-treatment of 500 nM PF-477736 for 3 h, followed by 4 Gy radiation increased apoptotic signaling, as compared to that seen upon irradiation alone. Cells were harvested 72 h post-irradiation. β-actin was used as a loading control. Densitometric analysis showed increased Bcl-2-associated X (Bax)/B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) ratio after the combined treatment. Enhanced apoptosis in response to combinatorial treatment with 500 nM PF-477736 and 4 Gy radiation in MDA-MB-231 cells (E) and Hs578T cells (F). MDA-MB-231 cells and Hs578T cells were pre-treated for 3 h with 500 nM and 100 nM of PF477736, respectively, followed by irradiation with 4 Gy of X-rays or protons. Cells were harvested 72 h post-irradiation and apoptotic population was determined as described in Materials and Methods. Quantification data were shown. Data are shown as mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.